Solved
Non-Sequential Optimization: Set Boundary Values
Hello,
this might be a stupid question, but I did not find a solution myself.
I am designing an optical system for my bachelor's thesis and want to optimize it.
Is there any possibilty to easily set boundary values in non-sequential mode like there is in sequential mode? Or to set a start/stop value like when doing a Universal Plot?
At the moment, almost all of my optimization attemts lead to impossible settings, like one lens inside the other or the detector placed right after the source.
I feel like there must be something I just have overseen.
Thanks in Advance!
this might be a stupid question, but I did not find a solution myself.
I am designing an optical system for my bachelor's thesis and want to optimize it.
Is there any possibilty to easily set boundary values in non-sequential mode like there is in sequential mode? Or to set a start/stop value like when doing a Universal Plot?
At the moment, almost all of my optimization attemts lead to impossible settings, like one lens inside the other or the detector placed right after the source.
I feel like there must be something I just have overseen.
Thanks in Advance!
Best answer by David
Hi Julia,
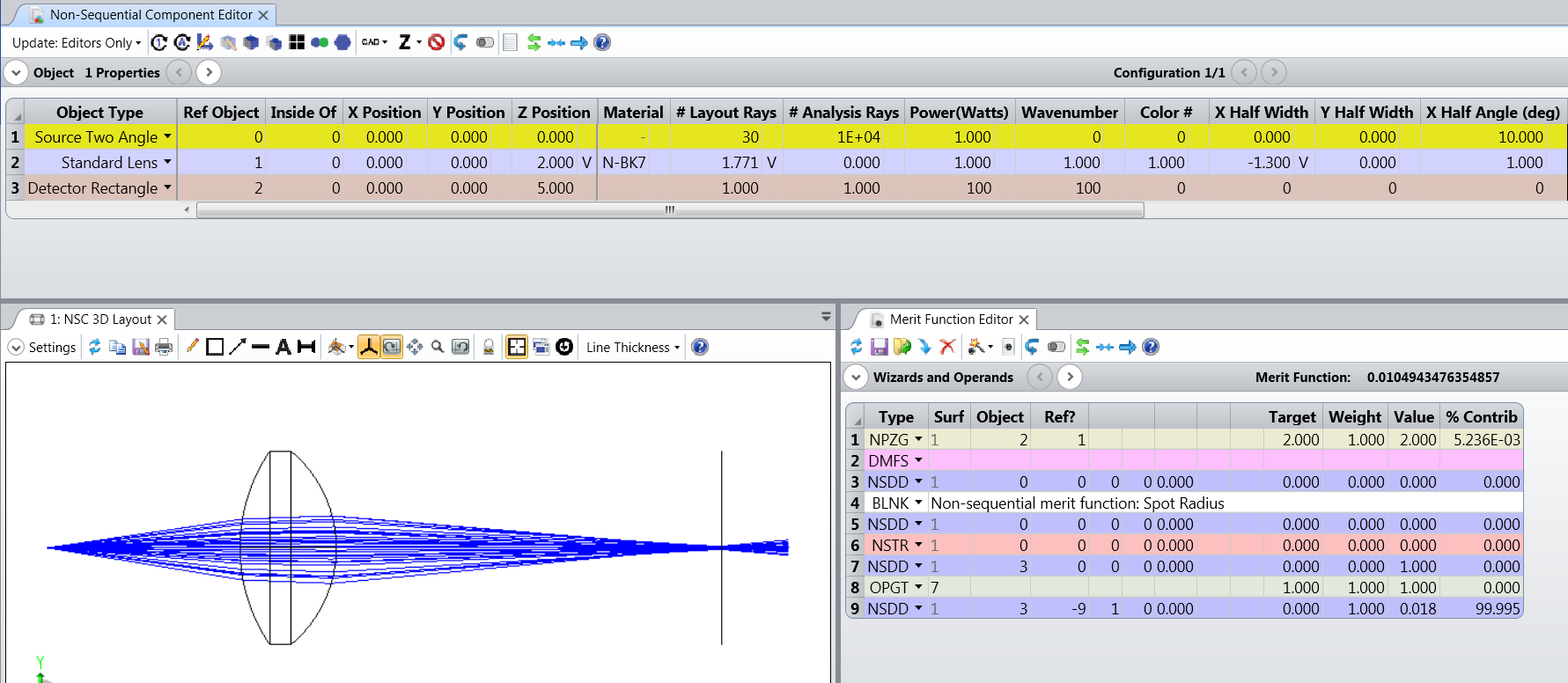
Look at the merit function section "Constraints on Non-sequential Object Data" in the help system. You will find merit function operands for non-sequential systems. For example: NPGT is non-sequential parameter greater than; NPLT for less than, NPVA for value. These and others can be used to constrain the design during optimization.
Kind regards,
David
View originalLook at the merit function section "Constraints on Non-sequential Object Data" in the help system. You will find merit function operands for non-sequential systems. For example: NPGT is non-sequential parameter greater than; NPLT for less than, NPVA for value. These and others can be used to constrain the design during optimization.
Kind regards,
David
Reply
Enter your E-mail address. We'll send you an e-mail with instructions to reset your password.