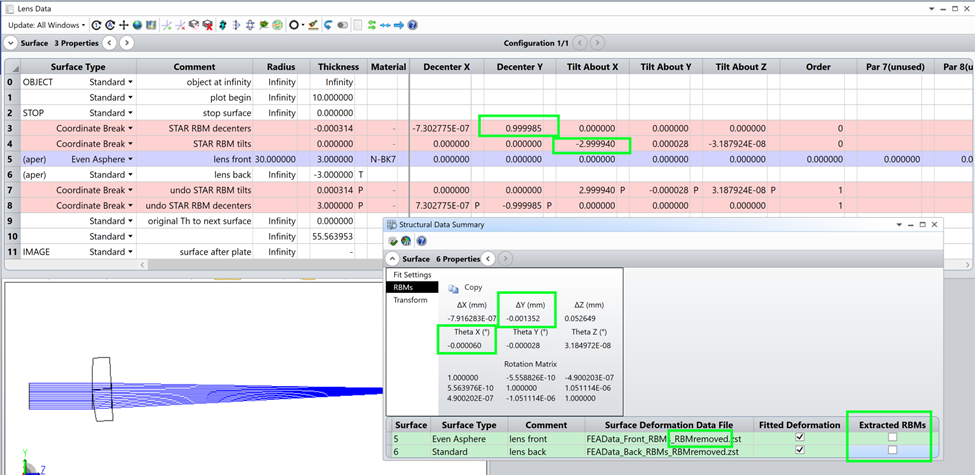
In STAR, the Component RBM tool allows us to extract RBMs for a lens or mirror and automatically convert them to coordinate breaks. Considering the FEA data on all surfaces in the optic, we calculate any RBMs that are common to the surfaces, to find the motion of the optic as a whole. The component-level RBMs are reported, and a button converts the common RBMs into Coordinate Breaks.
Currently, this is a one-way transformation, so users are prompted to save their original file before converting to Coordinate Breaks.
(Extracting RBMs can be carried out for each surface individually, as well, to accommodate mirrors. We could declare each surface of this lens as a separate component, and extract the RBMs for the front and back surface’s deformation data separately. Note that currently, nesting of RBMs is not officially allowed, though there are some clever workarounds possible.)
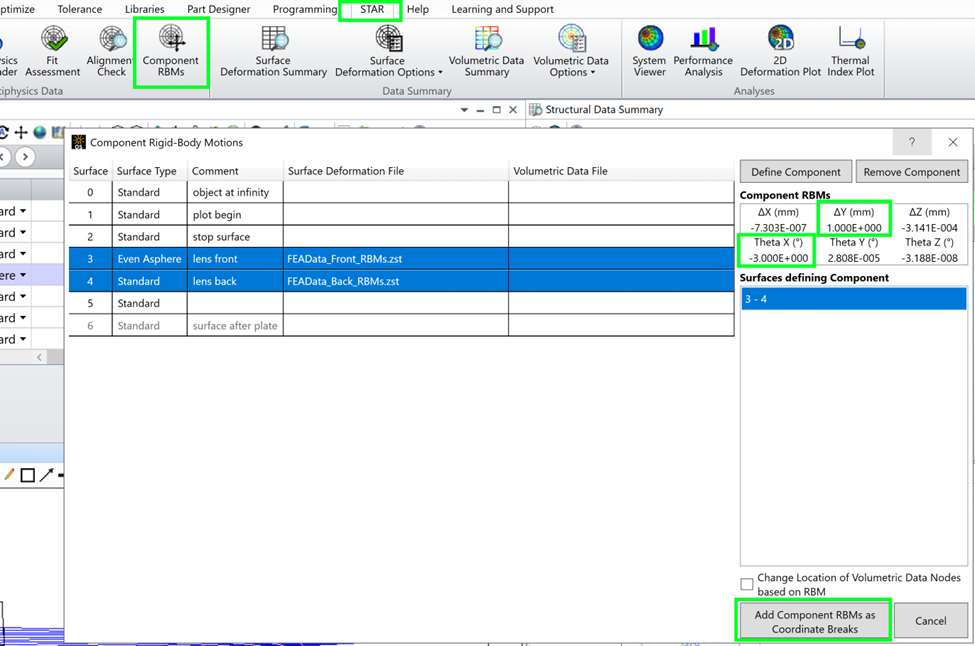
After removing the RBMs common to all surfaces that make up a component, any remaining RBMs on the individual surface are included in the new FEA data set. In the Structural Data Summary, the residual surface RBMs are now shown in the RBM property of the surface. The file names have also been altered to show that component-level RBMs are no longer included in the data.
Note that the “Extracted RBMs” column has been turned off! Since the component-level RBMs are now captured as coordinate breaks, the Extracted RBMs column must be turned off to avoid doubling the RBMs.