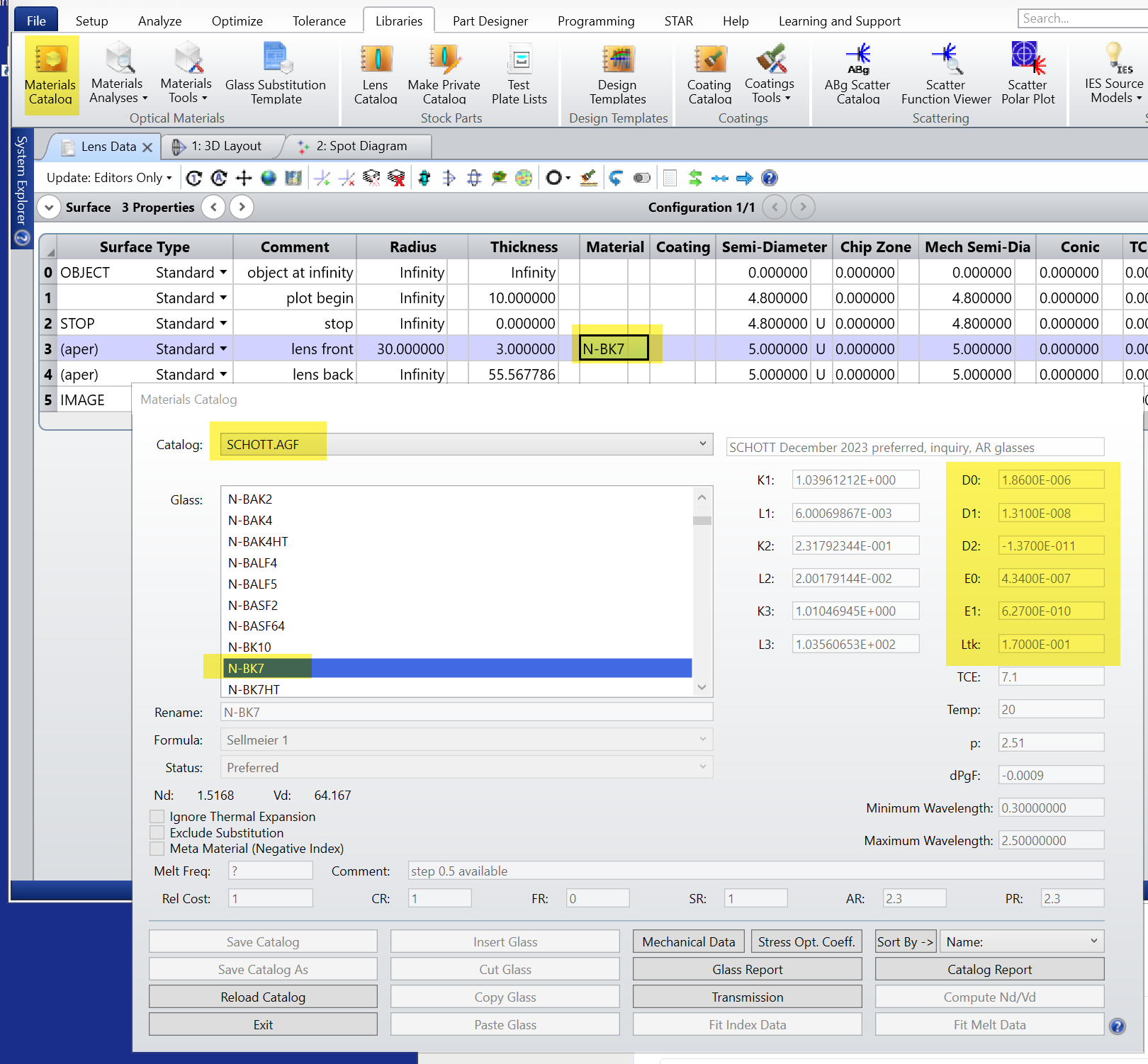
Hi, folks. One of our users asked about how temperature is converted into index of refraction. Raytracing inside Zemax is fairly complex; there is an explanation inside our Help files under “Index of Refraction Computation.” We use a formula developed by Schott.

The constants in the equation are in the material’s library data. Not all materials have a complete list of the coefficients. If a material only lists the D0 value, then the change in index with temperature is purely linear. That is okay in some situations; usually for temperatures near room temperature, where the D0 coefficient was likely measured. In general, though, the relationship is non-linear.
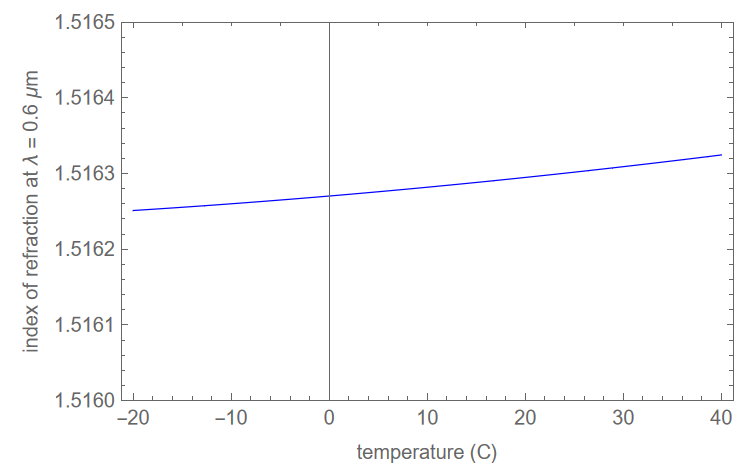
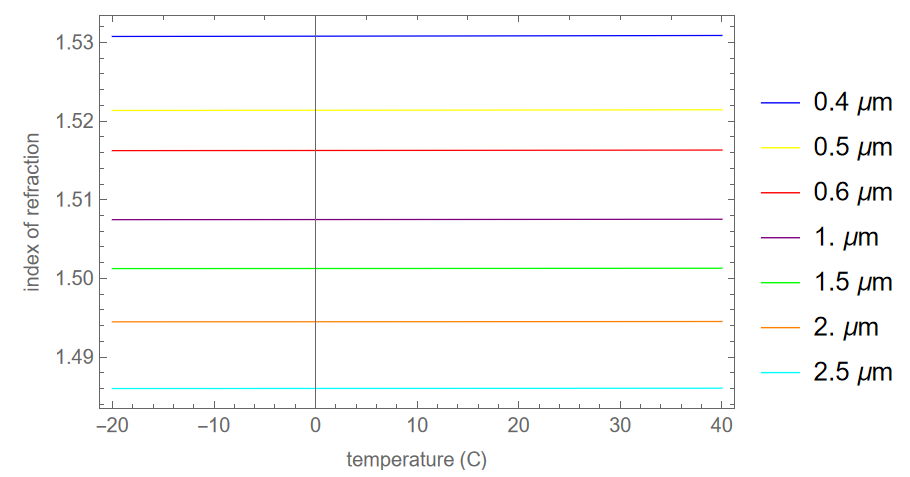
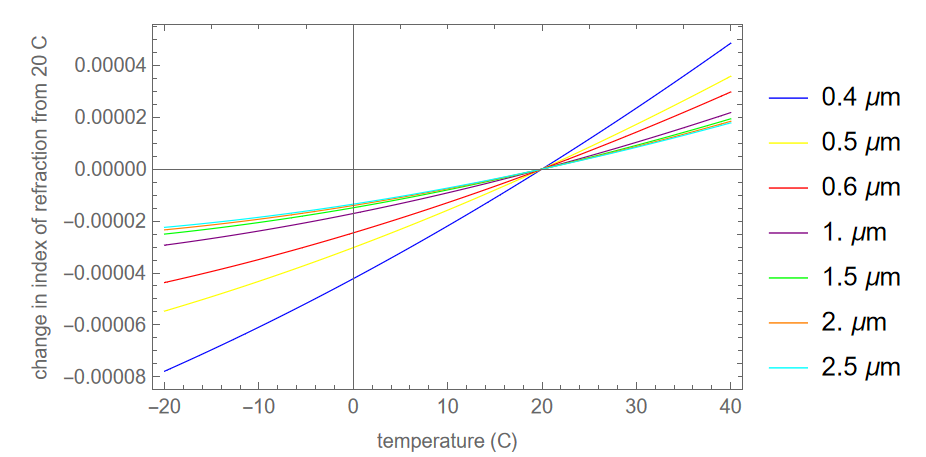
Because we don’t often look at how index behaves with temperature, here are a couple of plots for N-BK7. Index tends to rise slightly with temperature. The rising slope is much smaller than the change in index as a function of wavelength. And the index change is greater for shorter wavelengths.