Hi,
This is Oliver. I’m currently working on an optical fiber endoscope project, where minimizing back reflections is critical for our application in optical coherence tomography (OCT).
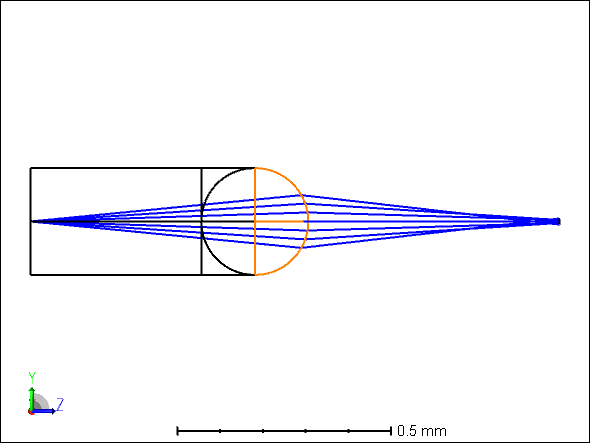
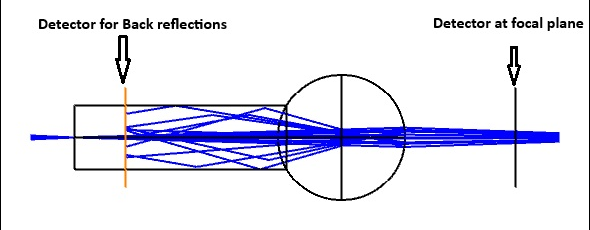
In particular, I’m looking to quantify the back reflections from specific lens surfaces—such as the ball lens-air interface highlighted in the attached figure. The system involves a single-mode fiber launching light through a segment of coreless fiber and a ball lens. The majority of the back reflections appear to originate from the ball lens-air interface.
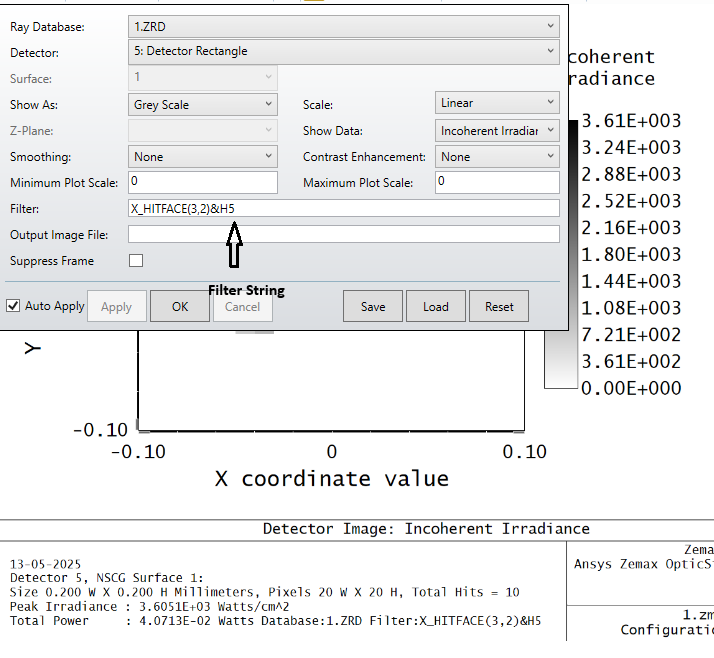
My goal is to use Zemax to estimate the amount of power reflected back into the single-mode fiber. For example, if the input power is 10 mW, is it possible to calculate the power reflected back toward the source in Zemax?
Ultimately, I plan to optimize the material and geometry of the ball lens to minimize these reflections. I’ve attached the Zemax file for your reference, and I would appreciate any guidance or suggestions on how best to approach this analysis.
Thank you for your help.
Best regards,
Oliver