hello all,
I am trying to simulate a two slab cavity absorption.
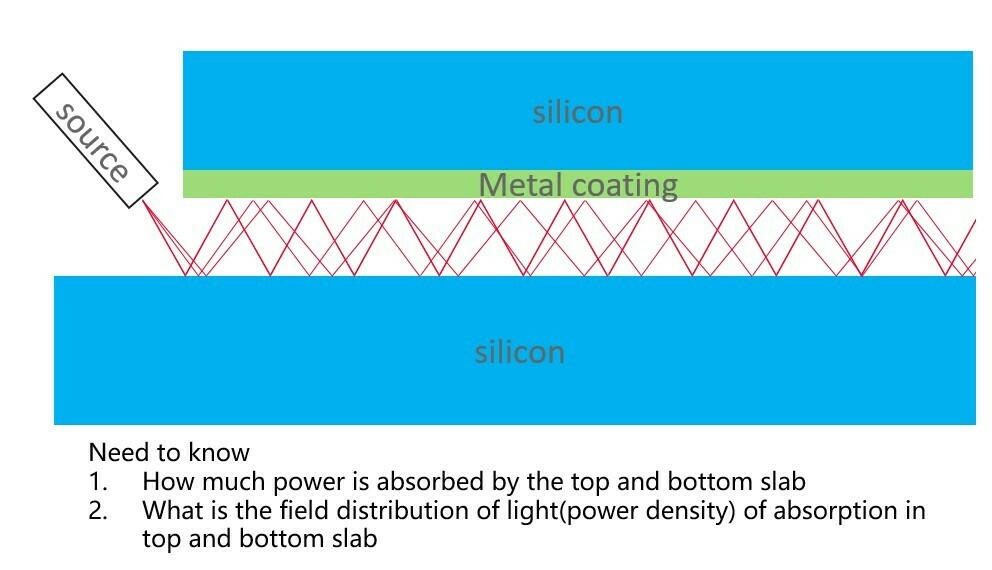
As shown in the picture, the light is emitted from the side of the cavity. and the top and bottom cavity are made of silicon, which has an complex refrective index in visible wavelength. and also the top slab is coated with Pt, which can reflect most of the light but still got around ~7% absoption.
My goal is to calculate
- How much power is absorbed by the top and bottom slab
- What is the field distribution of light(power density) of absorption in top and bottom slab
two issue I encountered now
- I dont know how to model a material with complex refractive index. It seems the transmission property of materials catalog do not deal with polarization and incident angle? And how about the absorption in metal coating?
- for the power density, I put a detecter in between the slabs, due to multiple reflection in the cavity, the total power it returns is larger than the input power of the source. By setting the detector ‘front only’could still not solve this issue.
Any idea how to model this absorptive cavity?