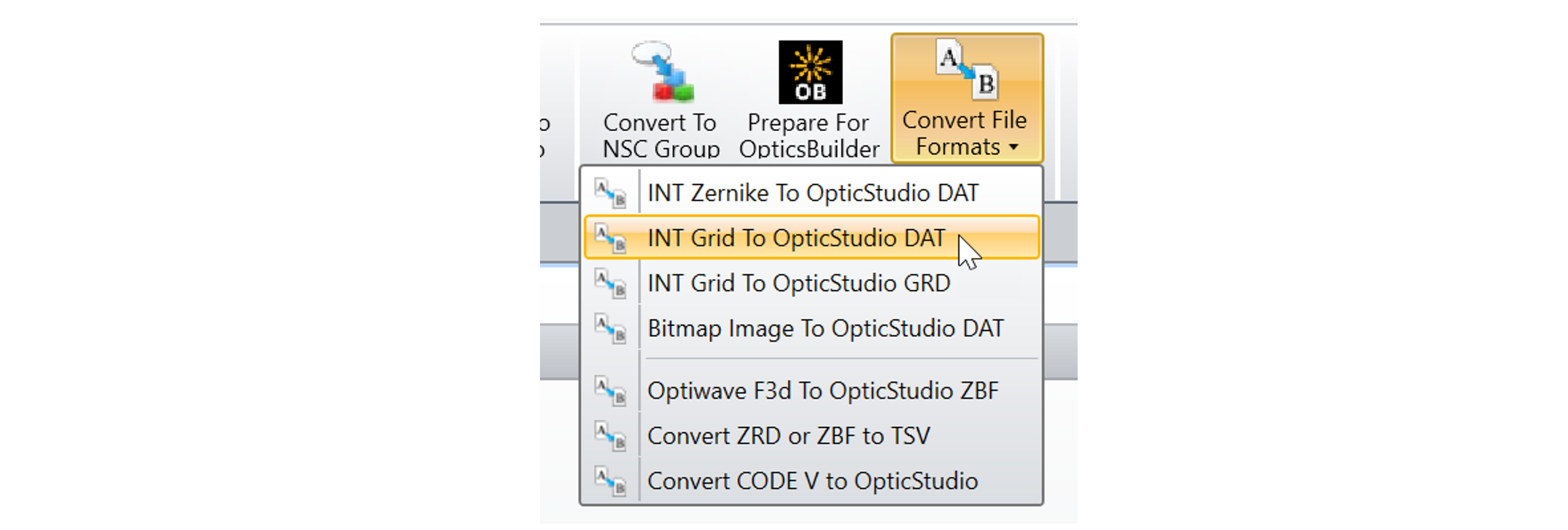
Measured interferometric data can be added to optical surfaces in OpticStudio using the Grid Sag surface. We provide an automated method for converting .INT files into the .DAT format used by the Grid Sag in the File/Convert File Formats tab, as shown below. This method works well when the optical surface being measured is a Standard or Even Asphere shape.
For other surface shapes, it was necessary to convert to a Grid Phase surface (which can cause XY position errors) or to place the underlying optical surface shape into the sampled data (which converts an analytic surface to a sampled one, for a loss of precision and speed during raytracing). Both methods also require data manipulation outside of OpticStudio.
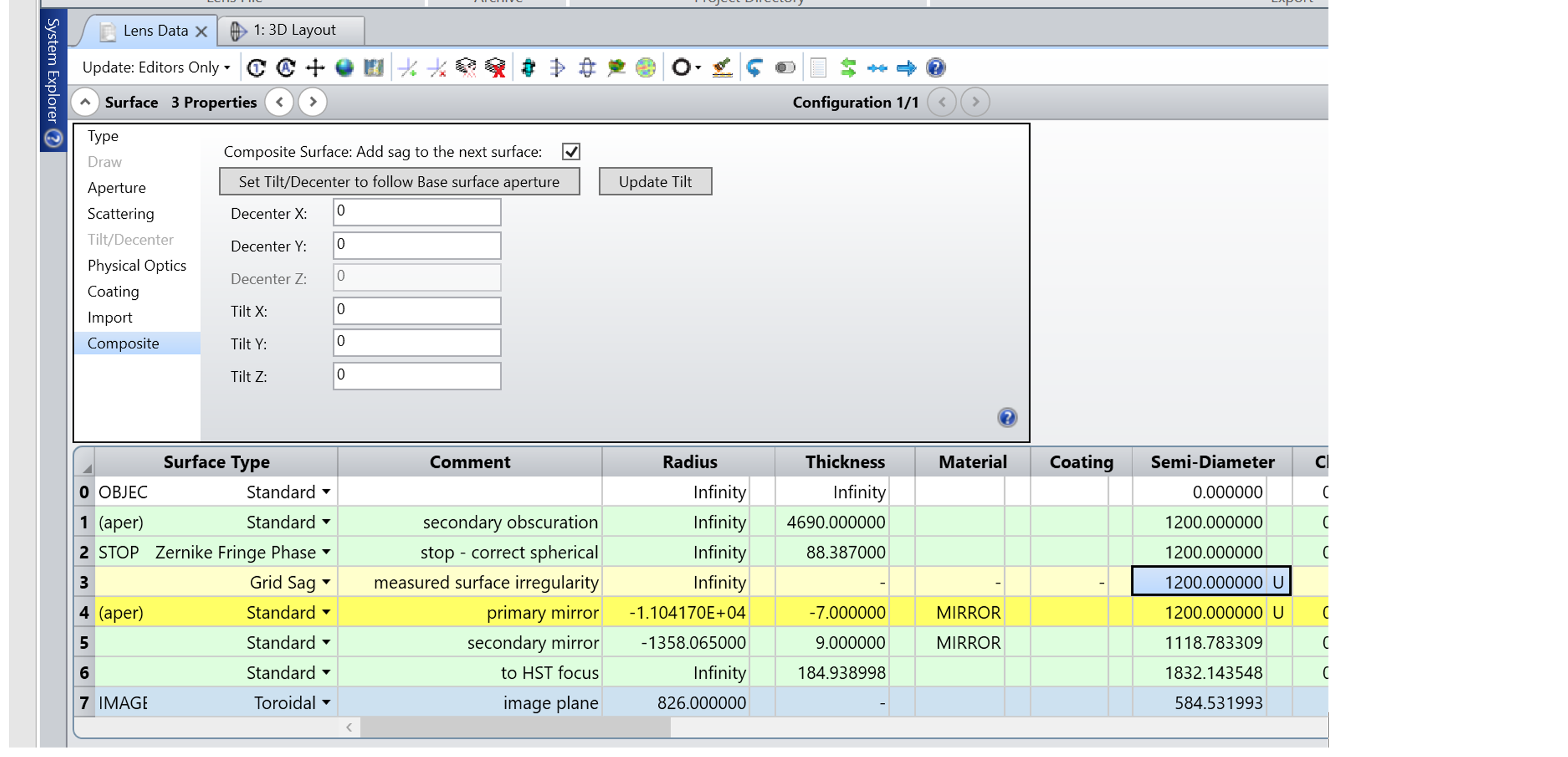
With the new Composite surface capability, interferometric data can be easily added to any surface shape, and the accuracy and speed of raytracing is preserved. Users can convert the data from .INT to .DAT as before, and then place a Grid Sag surface before the optical surface in the Lens Data Editor, as shown below. Then, turning on the "Composite" property adds the Grid Sag to the next surface, as shown below for the primary mirror of the Hubble Space Telescope. Now the measured data is added to the mirror surface, and the total sag is contained in surface 4. (The raytraces no longer interact with surface 3; just with the combined total sag in surface 4.)
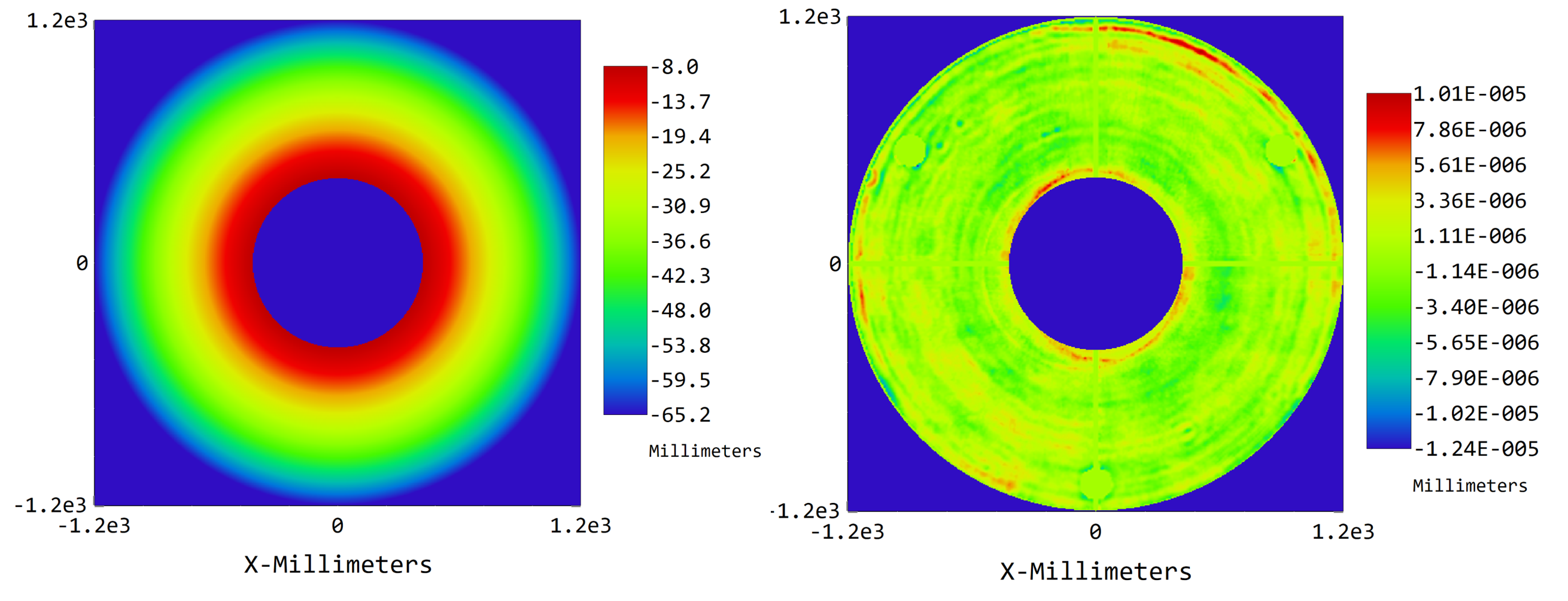
The sag map for the primary mirror can be seen by using Analyze/Surface/Sag Map. The sag is dominated by the ROC of the mirror, as shown below. But the interferometric data alone can be plotted by choosing Base Sag in the Remove option of the Sag Map’s settings. (The measured data shown is approximate.)