
July 12th, 2023
1 Tools, Features, and Capabilities
1.1 Project Directories: Fully Customizable Lens Projects (All Editions)
Easily manage and customize your design projects.
Project Directories enable easy packaging and storage of important Zemax files so that they can be accessed and manipulated on a project-by-project basis. A new Project Directory group was added to the File tab, providing standard Windows file management functionality tailored to the lens project files.
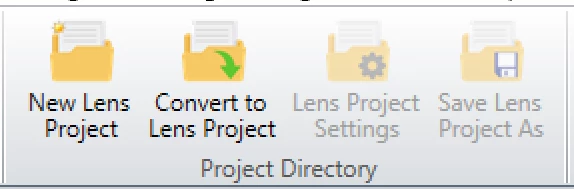
A Project Directory can be created either by starting a new lens design with the New Lens Project button or from an existing OpticStudio design by using the Convert to Lens Project button.
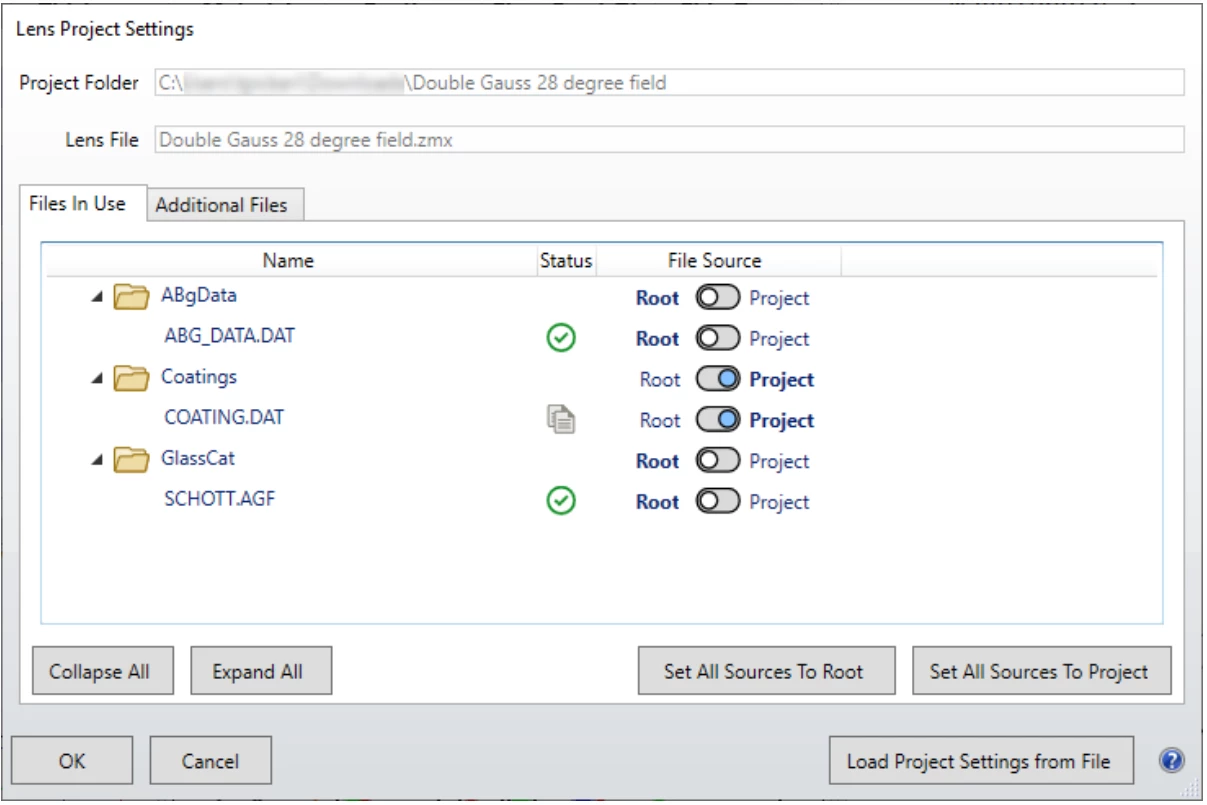
You can now customize lens projects and even link unsupported files so you can save and share complete projects. With the new Lens Project Settings, you can select the files specific to a project directory or to be loaded from the Zemax Data root folder. Additional auxiliary project files that contain information about the project but are not part of a lens file can also be added, such as specification PDF or data XLSX files.
Please note: In order to avoid confusion with Project Directories, the previously named Project Preferences are now called OpticStudio Preferences. The functionality remains the same.
1.2 Ansys Optics Launcher (All Editions)
Obtain trial licenses and get direct access to the Ansys Optics Application Gallery.
This tool is a launch pad for all your Ansys Optics applications. You can see the projects and files you have been working on and have links to set up your Ansys licenses. You also get direct access to Application Gallery examples from the Ansys Optics website, which provides a vast array of example simulation projects to get started quickly and easily.
You can also get an automatic 30-day trial license for either Lumerical or Speos, so you can experience our other industry-leading optics and photonics tools for free! You can find more details on how to obtain a trial license in this Ansys Optics article.
This tool is installed separately on your machine and can be found in the Start Menu in the Ansys Optics 2023 R2 menu.
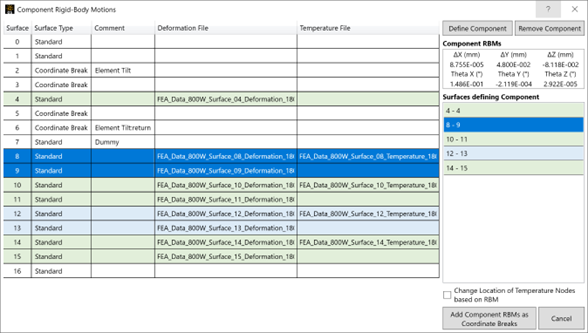
1.3 STAR: Component Rigid-Body Motions (Enterprise Edition)
Convert Rigid-Body Motions to Coordinate Breaks in the Lens Data Editor with just a few clicks.
This easy-to-use tool enables you to define an optical component (such as a lens or groups of lenses) and will calculate the tilts and decenters that comprise the component-level rigid-body motion (RBM). This component-level RBM can then be removed from the RBMs of the individual surfaces and added as a set of Coordinate Breaks around the surfaces in the Lens Data Editor with a single click. This enables you to perform tolerancing and optimization as part of your STOP analysis.
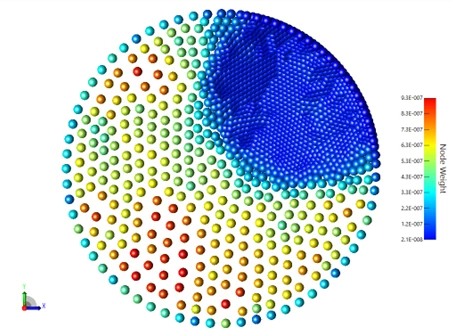
1.4 STAR: Support for Weighted FEA Data (Enterprise Edition)
Use Node Weights from FEA simulation for improved RBM calculatios.
The accuracy of rigid-body motions (RBMs) can be improved by using non-uniform node weights defined in the datasets saved from your FEA platform. This provides a more realistic representation of the RBMs and is especially useful when the FEA mesh is uneven or imbalanced. In addition, the Export to STAR ACT Extension for Ansys Mechanical has been updated to support the option to include node weights in the saved datasets.
1.5 STAR: Direct Index Fitting using ZOS-API (Enterprise Edition)
Expand OpticStudio’s workflow capability by loading refractive index datasets.
This release provides early access to new ZOS-API commands that enable you to load refractive index datasets into OpticStudio. The STAR fitting algorithm is used to create a non-uniform GRIN which is applied to the surface where the refractive index dataset is assigned. This expands the workflow types that OpticStudio supports with STAR functionality such as cases of modeling the impact of turbulent airflows on the performance of optical systems which are common in aero-optic applications.
1.6 Composite Surface: Support for Multiple Configurations (All Editions)
Easily tolerance surface irregularities now also for complex zoom lenses.
Introduced in Ansys Zemax OpticStudio 2023 R1, the Composite Surface capability enables you to easily create complex surface geometries in sequential mode by allowing the sag of any sag-based surface to be added to the sag of a base surface. This advanced functionality also allows for direct tolerancing of the surface irregularity of any sag-based surface without any workaround.
In Ansys Zemax OpticStudio 2023 R2, new Multi-Configuration Editor (MCE) operands were added to support multiple configurations for the Tilt and Decenter parameters in the Composite section of the Surface Properties:
- CSDX and CSDY for the Composite Surface Decenter in X and Y
- CSTX, CSTY, and CSTZ for Composite Surface Tilt in X, Y, and Z
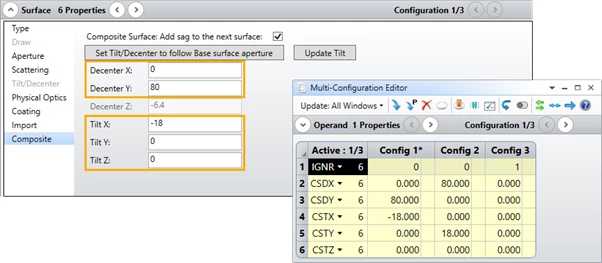
To turn the Composite behavior on or off for individual configurations, use the IGNR operand to ignore a specific Composite add-on surface.
1.7 Composite Surface: Support for Tools and Analyses (All Editions)
Improved setup, analysis, and export capabilities when using Composite Surfaces.
The following tools and analyses now fully support designs that include Composite Surfaces:
- Export to Speos Lens System
- Export CAD File
- Export Zemax Black Box
- Physical Optics Propagation (POP)
- Reverse Element
1.8 Export to Speos Lens System: ZOS-API Support (All Editions)
Automate your cross-product workflow.
The Export to Speos Lens System tool generates a reduced order model (ROM) that includes the relevant parameters of the optical system to enable accurate optical sensor simulation in a realistic environment within Speos. This model can then be used to integrate component-level designs into a comprehensive system simulation for rendering and visualization.
You can now set up and run the tool through ZOS-API. This enables automation of ROM creation and the streamlining of cross-product workflow. The interface to the tool can be found under ZOSAPI.Tools.IExportToSpeosLensSystem, which gives access to all settings and standard functions.
2 Performance and Stability Improvements
- Diffraction DLL: lumerical-sub-wavelength-dynamic-link-2023R2.dll – The dynamic link is now faster and more stable in case of running large number grating variations, e.g. when there are many wavelengths or when the system is being optimized.
- Diffraction DLL: lumerical-sub-wavelength-dynamic-link-2023R2.dll – Any parameter changes in OpticStudio are now immediately reflected in the Lumerical UI so that you don't have to wait to run a ray trace to see the new geometry of the grating.
3 Libraries and Catalogs
3.1 Parasolid CAD Libraries (All Editions)
Parasolid libraries replace previously existing ACIS CAD libraries.
OpticStudio now utilizes Parasolid CAD libraries to create faster and more accurate optical geometry. This aligns with the new Parasolid support found in OpticsBuilder and existing Parasolid support within Ansys Speos.
The Parasolid libraries are used by default. If you uncheck the options in the OpticStudio Preferences > General, OpticStudio will revert back to SMS libraries.
3.2 ISX and RSMX Libraries (All Editions)
Deprecated Integrated Scatter Catalog and Radiant Source Models removed from OpticStudio.
With the 2023 R1 release, the RSMX and ISX libraries were deprecated. The reason for deprecation is that these libraries rely on obsolete Microsoft components that could potentially introduce IT or security vulnerabilities in the future. These libraries and any functionality relying on them are now completely removed in the 2023 R2 release. This includes the following features:
- Download Radiant Source Models
- View Radiant Source Models
- Generate Rays
- Reverse Radiance
- IS Scatter Catalog
In addition to the features listed above, the REVR Merit Function Operand and the ReverseRadiance Detector and Target objects have also been removed.
To replace the ISX libraries, new BSDF scatter libraries will be made available in Ansys Zemax OpticStudio in a future release, based on a format that can be easily updated and maintained in a secure manner.
4 Bug Fixes
- STAR FEA Data Viewer – The FEA Data Viewer on the STAR tab now retains the displayed data when saving and reopening a lens file.
- Standard Spot Diagram – Fixed an issue where the afocal units from the System Explorer were not correctly reflected in the Spot Diagram
- NSC Ray Trace – Ansys Zemax OpticStudio now correctly saves the number of cores set by the user when using the NSC Ray Trace tool instead of reverting back to the default value.
- Gradient Index DLLs – Improvements were made for sequential mode GRIN ray tracing efficiency, including for User Defined Surfaces with gradient index of refraction and for cases where an aspheric surface follows the GRIN material. For efficiency purposes, some limitations are imposed during the GRIN ray intercept calculation that may cause rays to terminate prematurely in niche cases such as when a ray reverses direction inside of a GRIN medium. Please contact customer support if you run into unexpected sequential GRIN ray trace problems.
- STAR Fit Assessment tool – If the Max Level value was set to a value greater than 16 then the tool would revert to the default value of 8. Now the setting will remain at the maximum of 16.
- Convert to NSC tool – Fixed an issue where converting a sequential Extended Polynomial surface to the corresponding NSC object resulted in an incorrect shape.



