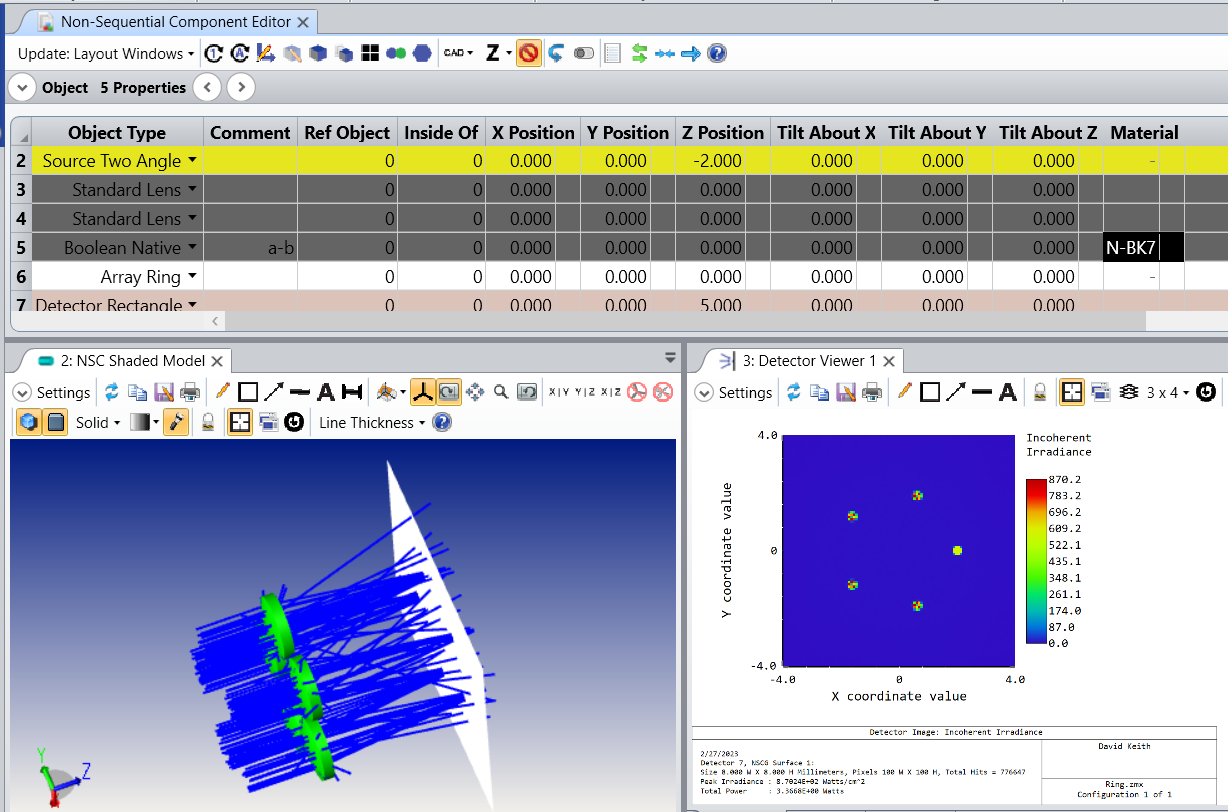
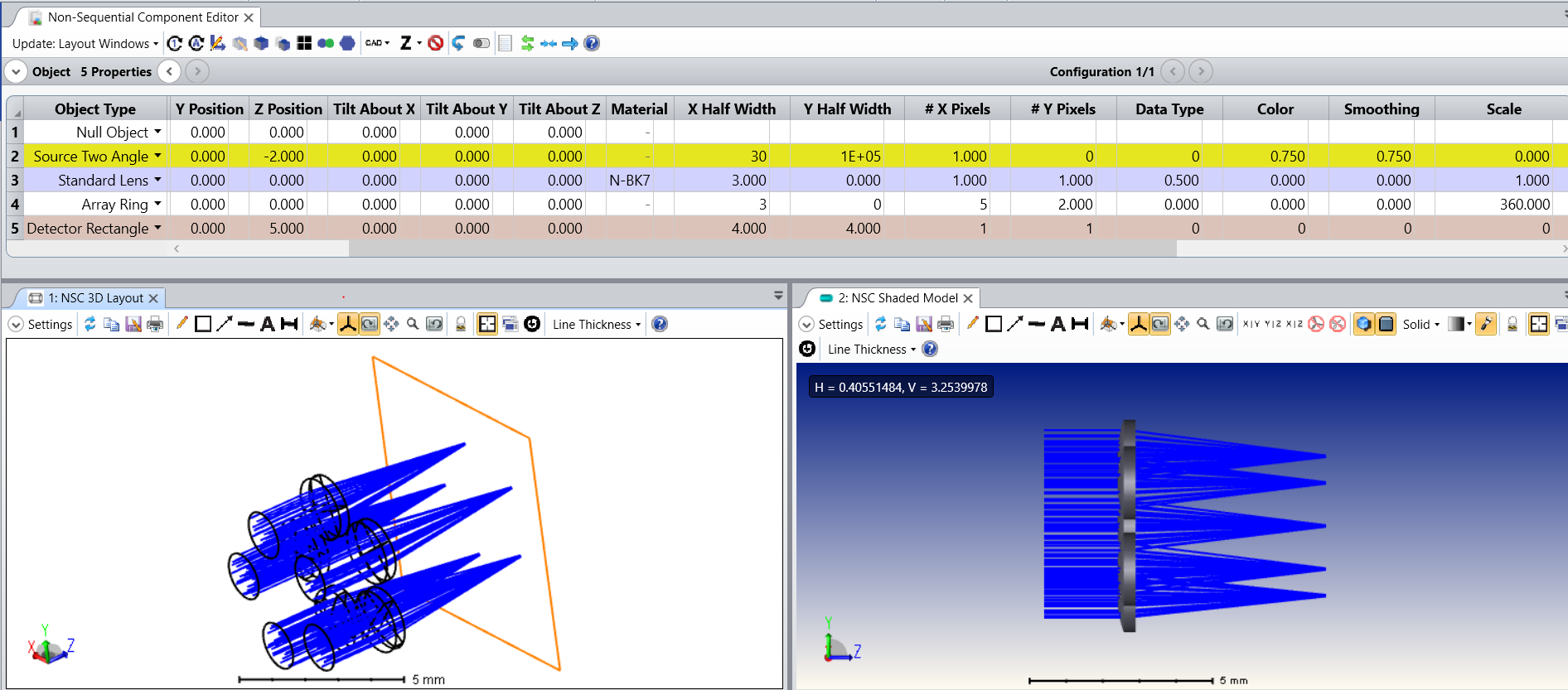
I generated a circular array of 16 radial sources using the Object properties in the non-sequential component editor. It automatically generates each at distributed angles in the circle. I need to place optical elements on each and I wanted to ask how can each source’s location be found?
Thanks,
Niel McCaffrey
[Mod note: moved to more appropriate forum for OS-related discussions.]