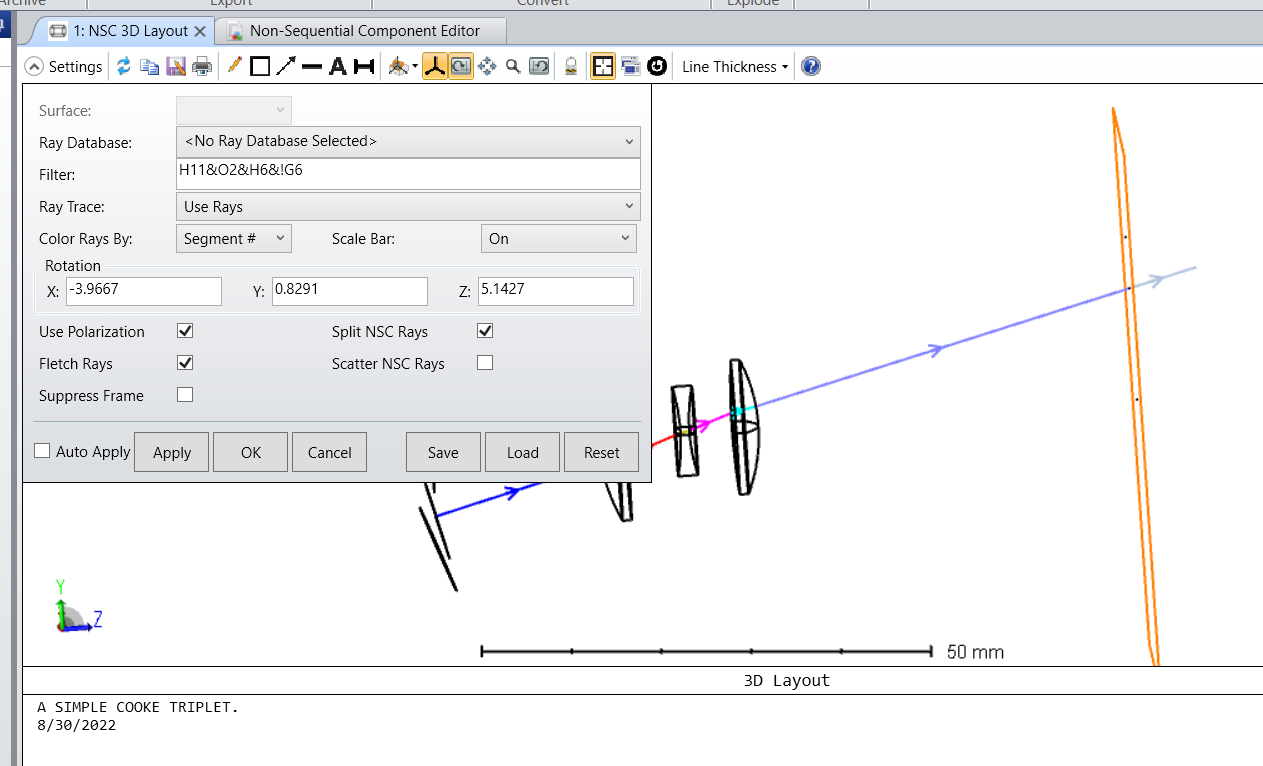
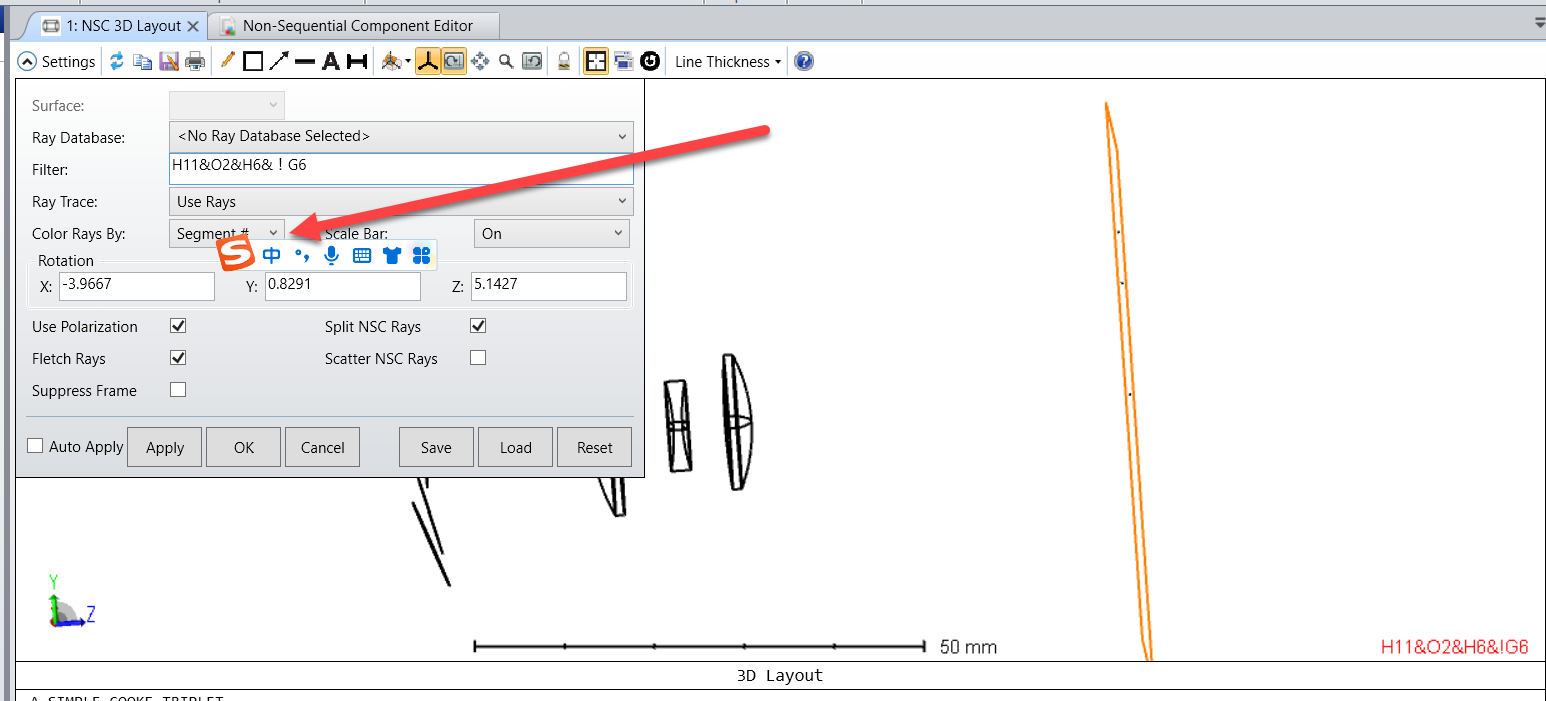
What shall I do to get ghost rays separated from transmitted rays that hit certain objects?
How to separate ghost rays
Best answer by yuan.chen
We can use filter strings to select rays.

They are mentioned here: The Setup Tab > Editors Group (Setup Tab) > Non-sequential Component Editor > Non-sequential Overview > The Filter String
A general introduction can be found here:
Identifying specific rays using filter strings – Knowledgebase (zemax.com)
This article shows the specific application of Gn and Hn in ghost image analysis.
Introduction to stray light analysis - Part 2 – Knowledgebase (zemax.com)
They belong to the stray light analysis path.
Stray Light Analysis – Knowledgebase (zemax.com)
Besides, we have an advanced stray light analysis example made by our excellent engineer Michael.
Stray light analysis for Head-up-Display - Part 3 – Knowledgebase (zemax.com)
Enter your E-mail address. We'll send you an e-mail with instructions to reset your password.