The STAR Module in Ansys Zemax OpticStudio allows users to import FEA datasets and analyse their impact on optical performance. In some optical systems, the load cases on the image plane can significantly affect this performance. For example, a lateral shift of a detector or receiving fiber due to the expansion of the housing in an optomechanical system may have a considerable influence. I`d like to briefly demonstrate how this can be addressed within a STOP workflow using Ansys software packages:
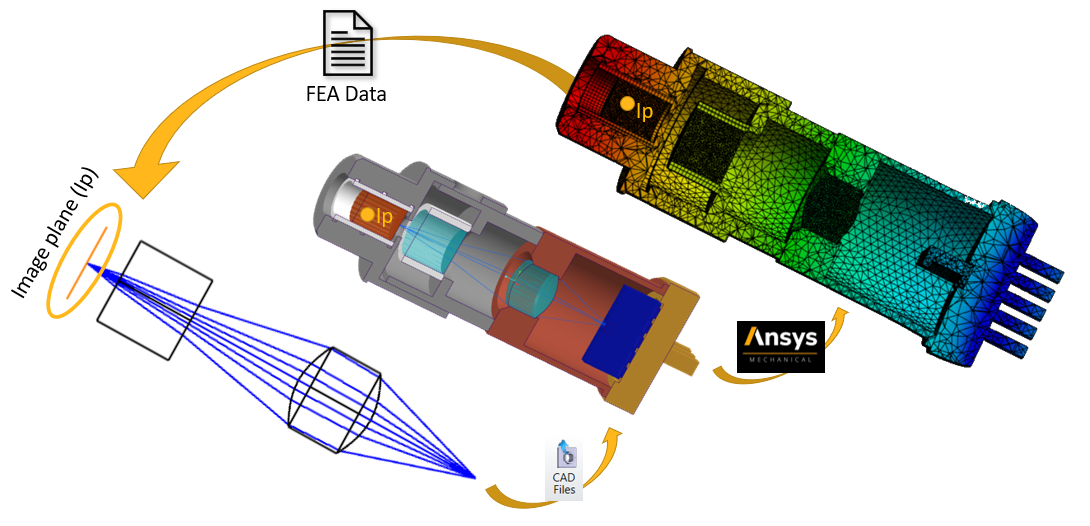
On the left, as a starting point, we have an optimised optical system for a transceiver. These types of optical transceivers are widely used in fiber optics communication systems. The geometry is then exported into a CAD environment, where the housing for the transceiver is designed. At this stage, we also design the initial section of the receiving fiber, which represents our optical image plane, as a physical geometry (labelled as Ip in the graph above). The diameter of this geometry should match that of the image plane in OpticStudio, and it should be positioned relative to the last physical optical surface in the same way.
The optomechanical system is then imported into Ansys Mechanical, the FEA software used in this workflow. Within Mechanical, we can simulate the thermal expansion of the entire system. The receiving fiber geometry is meshed, and the deformation data for the front surface of the fiber can be generated. This dataset is then assigned to the image plane via the STAR Module. OpticStudio’s analysis tools will subsequently account for any lateral shift and deformation on the image plane.



