Hello Ryoji,
The difference is in how the input beams are setup.
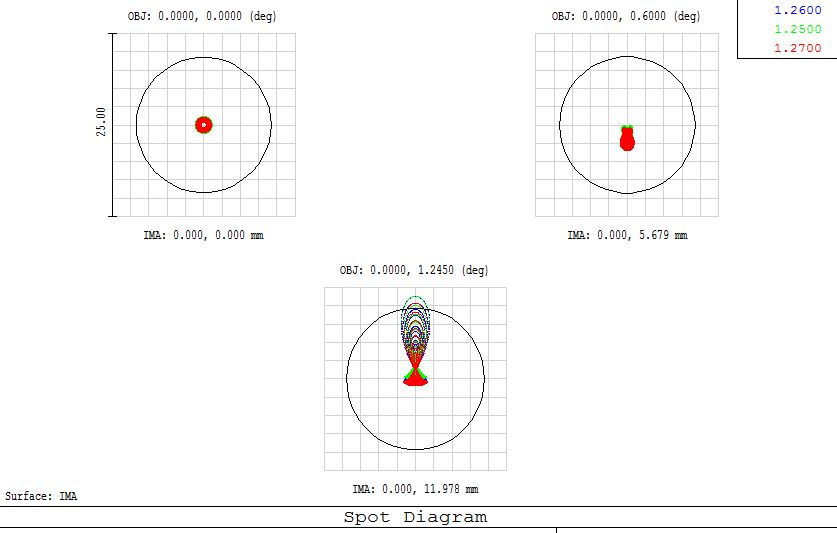
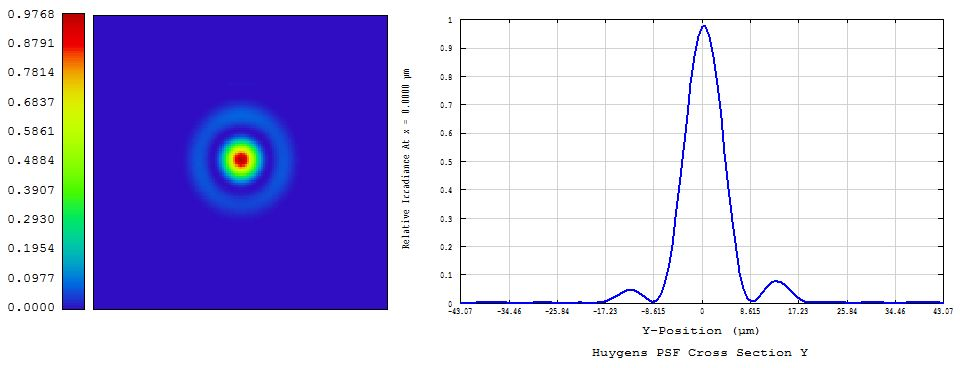
In the ray-based model, you have uniform pupil apodization, so the pupil is uniform and circular. When you take the FFT of a disk, you get the Bessel function shape we recognise as a 'diffraction pattern'.
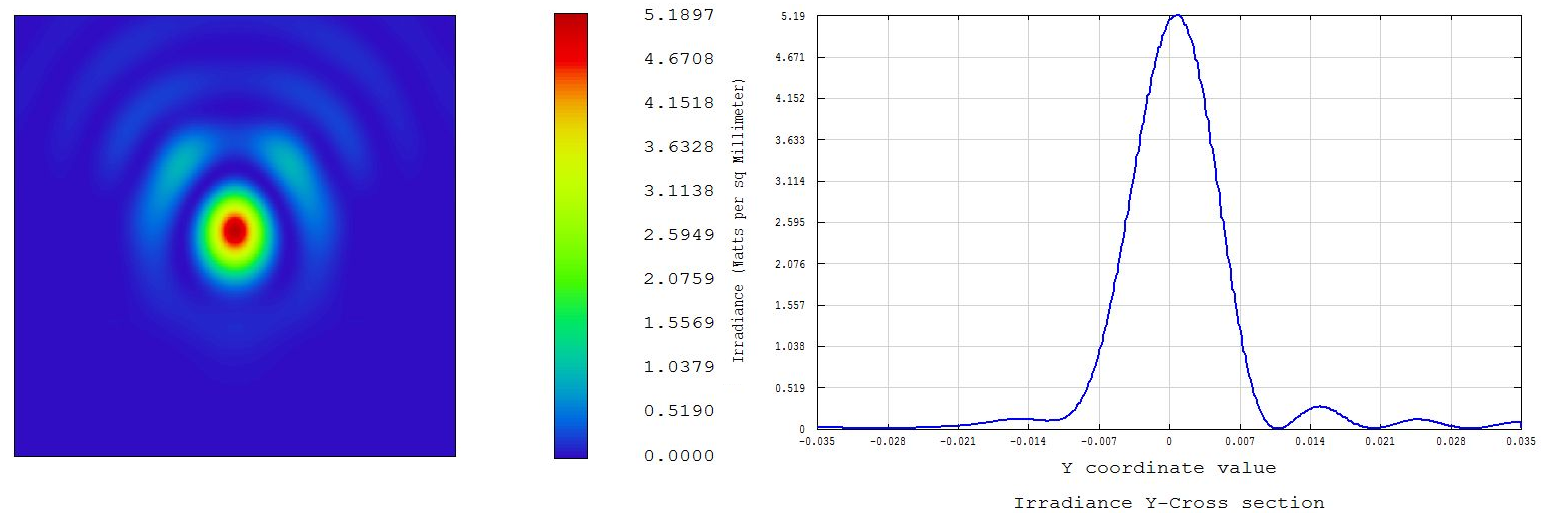
In the POP model you are modeling the input beam as a Gaussian, and the Fourier transform of a Gaussian is still a Gaussian. A diffraction-limited Gaussian is still smooth and has no secondary structure.
So both are 'correct' but they are set up differently. If you want the Gaussina illumination in your ray-based moel, change the apodisation type from Uniform to Gaussian. If you want the uniform pupil in the POP analysis, change the Beam Definition to 'Top Hat' from its current Top Hat setting.
In this system, the FFT results are fine so the POP results will be the same but will take longer to calculate.
- Mark