
2024 R2.02 Release Notes
September 11th, 2024
1 Tools, Features, and Capabilities
1.1 Stress Birefringence Addition (Enterprise edition)
STAR tools support Stress Birefringence data and analysis
Stress Birefringence is a consequence of mechanical stress acting on a transmissive optical material due to the photoelastic effect. It is a physical effect that is becoming increasingly relevant for complex systems using injected-molded lenses, such as automotive HUDs, augmented reality headsets, and cell phone camera lenses. Many of these systems are sensitive to polarization changes throughout the optical path including those that come from internal stresses due to the manufacturing process or mechanical stress from the optic's mounting. The effects of these stress-induced polarization changes can now be imported into STAR so that you can model the effects of stress birefringence. New options in the STAR Performance Analysis and STAR System Viewer enable you to monitor the effects.
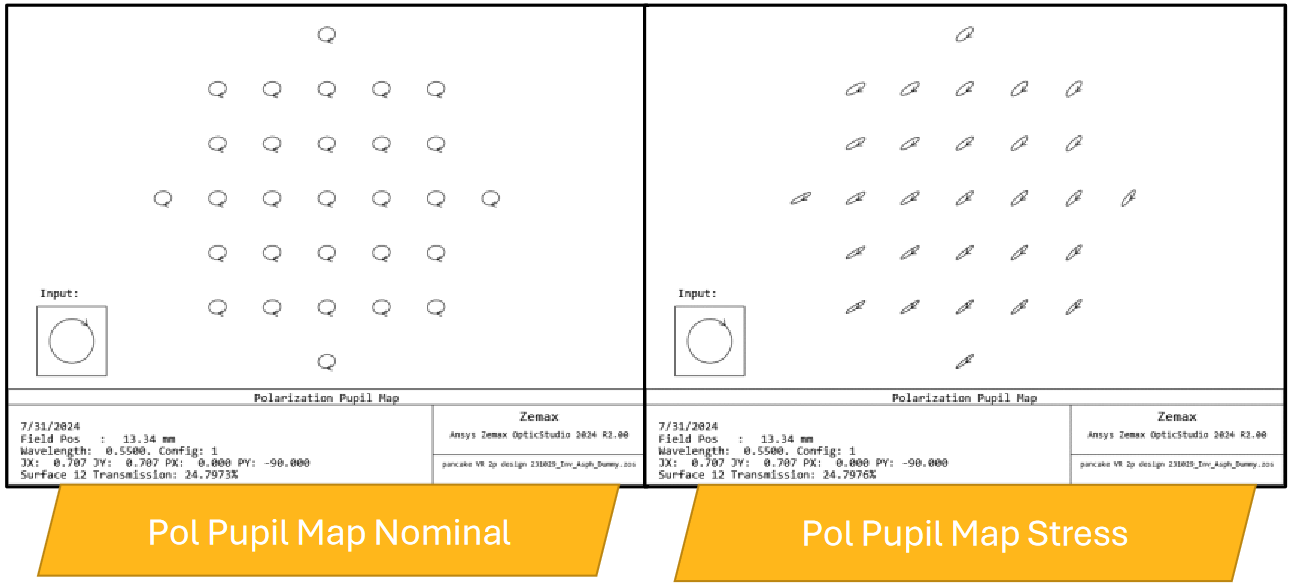
The image above depicts the OpticStudio Polarization Pupil map in the nominal optical system (left) and the stressed optical system (right). The effects of stress birefringence can be quantified using standard OpticStudio analyses as well as the STAR System Viewer and STAR Performance Analysis tool.
1.2 Composite Surface: Support for Convert to NSC (All editions)
Composite Surface available in non-sequential mode
Support has been added for translating Composite Surfaces into non-sequential equivalents via the 'Convert to NSC Group' tool. During the conversion process, the sequential total composite stacked sag is translated into the equivalent Grid Sag Surface for the front or back face of the non-sequential Compound Lens object. This enhancement enables more flexible NSC simulations and analyses by further supporting the Composite Surface.
1.3 LSWM Static Link – XY Spatial Variation Support (All editions)
LSWM now supports spatial variations of gratings
The LSWM Static Link plugin has been updated to support gratings that vary spatially on the substrate. Grating shapes, period, and direction can be a function of the Cartesian or Polar coordinates. Similar to the existing workflow, data needs to be generated from Lumerical in a file with extension filename .json. The file format is now updated to support spatial variation. More details can be found in Lumerical Sub-wavelength Model: Introduction and Data Generation – Ansys Optics.
1.4 Export Ray Footprint to CAD (All editions)
Ray Footprints help to prevent unintended optomechanical interference
In Sequential mode you may now export a ray footprint as layer onto a CAD object. In the Export CAD File tool, a checkbox allows you to add this export to your CAD file along with a drop-down to designate the layer it is saved to. Once the checkbox is selected, the Export CAD File tool ignores the number of rays and the ray pattern settings, and it will combine all wavelengths to give the outermost footprint of the ray as it intersects with the optical surface. A ray footprint will be generated for each field on each optical surface. This ray footprint CAD export can be passed on to your CAD-user counterpart for the purposes of designing the optomechanical enclosure outside of the active zone and avoiding unintended image contamination, TIR and vignetting.
1.5 ISO-10110 Drawing Improvements (All editions)
Optical tolerancing and lens geometry data enhancements to the ISO Drawing Tool
With these new updates to the ISO-10110 Drawing tool, you will find new values and updated behavior to the LDE & TDE import. In the TDE import, a new surface tolerance form format has been implemented on ISO10110 prints as 3/ A units (B units / C units) RMSx < D units. Accordingly, the tolerance operands for TIRR/TEZI/TCUR/TRAD/TFRN import behavior have been updated. The ISOA, ISOB, ISOC, and ISOD tolerance operands are supported. In the LDE import, Sag value and Marginal lens thickness (MLT) are auto populated.
You will also find UI updates to the ISO-10110 Drawing Tool including improved button labels, added tooltips, a new comments field, and a display of TWAV and Sag values in the ISO 10110 prints layout.
API export options have been added for ISO drawings to be saved in JPG and PNG and enhancements to the export of sag/MLT/surface form tolerance values have been included to the XML file.
1.6 STAR GRIN performance improvements (Enterprise editions)
Faster Performance of STOP Analysis with Thermal and Direct Index GRINs.
Performance improvements were implemented for STAR Thermal and Direct Index GRINs improving the calculation speed for your STOP analysis. Calculations that require GRIN ray tracing are more efficient for all STAR systems that utilize these multiphysics datatypes. There are no settings to enable, simply load your Thermal or Direct Index datasets and use the analyses in OpticStudio to realize the speed increases.
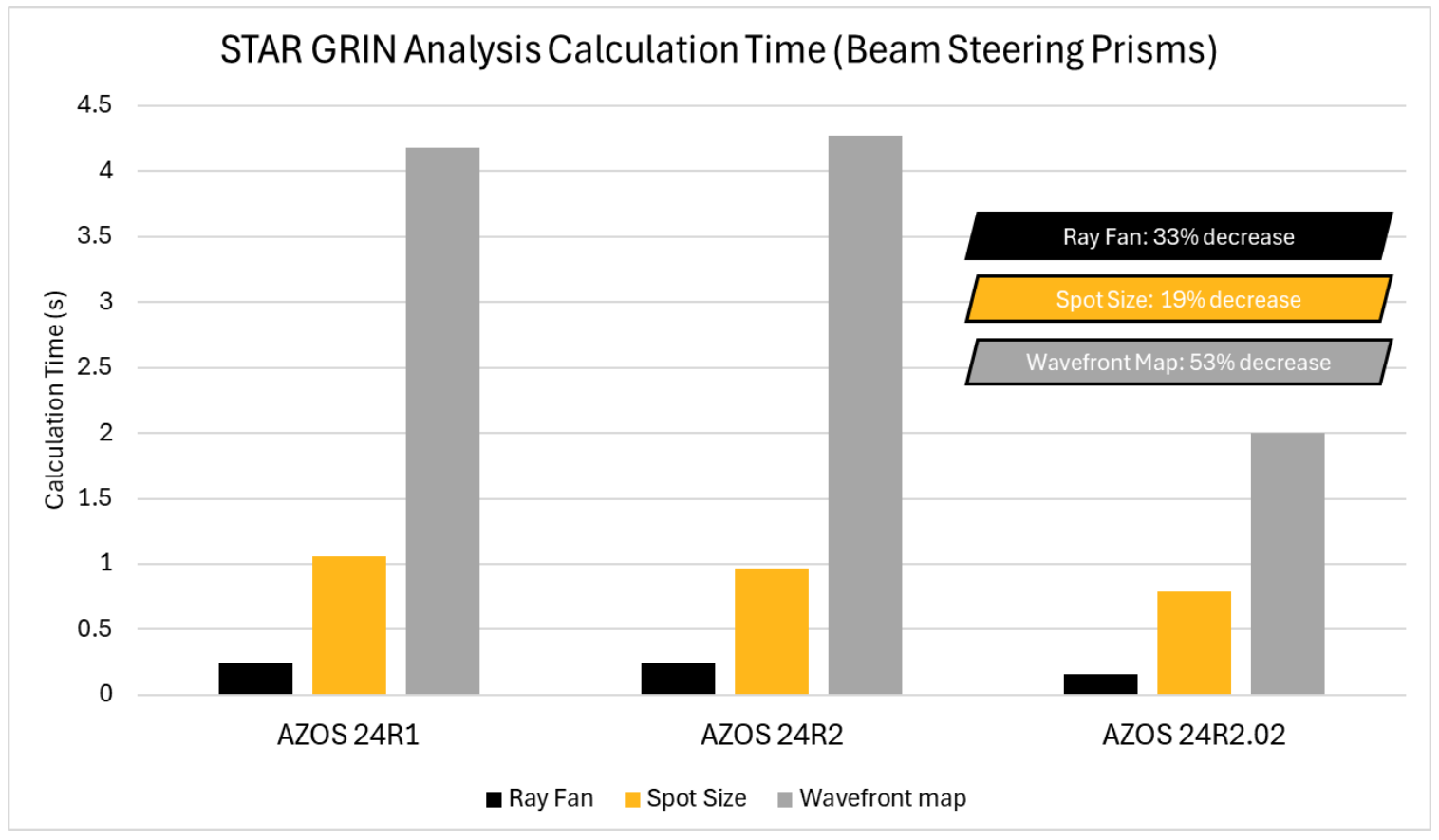
The graph above demonstrates the calculation time decrease for the beam steering example file that has 7 structural deformation files and 3 thermal files loaded to the optical surfaces. Calculations were performed on a light-duty laptop.
1.7 CAD Unit Settings
Correctly scale your geometry with CAD unit settings
CAD units define the unit of measure for all CAD geometry in OpticStudio. The setting determines how geometry is scaled when performing any operations using the Parasolid libraries. When creating geometry in Parasolid, OpticStudio will account for the scale difference between OpticStudio and Parasolid at all 'interface' points between them. Any exported CAD files will be created using the specified CAD units, except for native Parasolid files which will always be created in meters.
By default, the CAD units will be the same as the lens units resulting in no scaling of geometry between OpticStudio and Parasolid.
1.8 Cost Estimator Updates
Cost Estimator updates simplify the tool
The Cost Estimator tool has been removed from the Production Tools group found under the Tolerancing Tab of OpticStudio's main menu. You can still get real-time cost estimates using the ISO Element Drawing. These changes will simplify the Cost Estimator tool and enable better maintenance on the improved ISO Element Drawing itself.
In addition, LaCroix has been removed as a provider for the Cost Estimator to streamline their customer experience. LaCroix continues to be a valuable partner and collaborator to Ansys Zemax OpticStudio.
2 Performance and stability improvements
2.1 LSWM Dynamic Link Improvement (All editions)
Enjoy a cleaner, more seamless experience with LSWM.
We’ve made an exciting improvement to the LSWM dynamic link with the Lumerical plugin, significantly enhancing your user experience. Previously, the system reopened the Lumerical window after every 500 RCWA calculation calls, which, while functional, led to multiple empty Lumerical windows appearing during optimization. This was initially a workaround for a memory leak issue, but now that the underlying issue has been resolved, we've streamlined the process. With the latest update in the Lumerical-sub-wavelength-dynamic-link-2024R2-2.dll, this behavior has been removed, ensuring a smoother and more efficient workflow.
3 Libraries and Catalogs
3.1 File Updates (All Editions)
Updates to NHG material catalog and a new vendor, SALIENCE, added
Materials:
- New material vendor SALIENCE catalog is added for advanced optical design.
- New glasses added: H-LAF1S, H-LAF2S, H-LAF3B, H-LAF4S, H-LAF5S, H-LAF6S, H-LAF10S, H-LAF50S, H-LAF51S, H-LAF52S, H-LAF53S, H-LAF54S, H-LAF55S, H-LAF62S, H-LAK1S, H-LAK2S, H-LAK3S, H-LAK4S, H-LAK5S, H-LAK6S, H-LAK7B, H-LAK8S, H-LAK10S, H-LAK11S, H-LAK12S, H-LAK50S, H-LAK51S, H-LAK52S, H-LAK53S, H-LAK54S, H-LAK59S, H-LAK61S, H-ZLAF3S, H-ZLAF4LS, H-ZLAF50S, H-ZLAF51S, H-ZLAF52S, H-ZLAF53B, H-ZLAF55D, H-ZLAF56S, H-ZLAF66S, H-ZLAF68A, H-ZLAF68N, H-ZLAF69A, H-ZLAF71S, H-ZLAF75S, H-ZLAF76S, H-ZLAF78A, H-ZLAF89S, H-ZLAF90S, H-ZLAF92S, H-ZF7S, H-ZF13S, H-ZF52S, H-ZF62S, H-ZF71S, H-ZF72S, H-ZF88S, H-ZPK1S, H-ZPK2S, H-QK3LS, D-K9S, D-K9S-25, D-ZK2S, D-ZK2S-25, D-ZK3S, D-ZK3S-25, D-LAK6S, D-LAK6S-25, D-LAF53S, D-LAF53S-25, D-ZLAF52S, D-ZLAF52S-25
- NHG
- Compared to the 2023 product manual, the new version of the manual has undergone the following main changes:
- Materials
- 10 new materials have been added: H-PK71, H-LaK8B, H-ZF4AGT, H-ZF76, H-LaF3C, H-ZLaF60A, H-ZLaF76A, H-ZLaF80A, H-ZLaF82GT, H-BiF200.
- Materials have been set to obsolete: H-ZLaF66GT, IRG102, IRG104.
- Transparency Performance Adjustments
- The material H-ZLaF70B has improved coloration and internal transmission standards.
- Mechanical Property Adjustments
- Five automotive materials have updated their flexural strength: H-LaF50B, H-ZLaF50, H-ZLaF64, H-ZLaF68A, H-ZLaF72.
- Relative Price and Production Frequency:
- The relative prices and production frequencies for some materials have been updated.
- Materials
- Compared to the 2023 product manual, the new version of the manual has undergone the following main changes:
4 Bug Fixes
- NSC Surface Sag analysis silently modifies ray trace settings - Running the NSC Surface Sag analysis previously had the potential to alter certain system-level NSC Ray Trace settings. This issue has been resolved, guaranteeing that these settings remain unchanged after the analysis is completed.
- Zernike vs. Field analysis gives wrong values - Fixed an issue with the Zernike vs Field analysis where certain types of solves, such as Chief Ray solves, would lead to incorrect calculation results.
- Compound Lens Generates Incorrect Shape with Biconic Zernike Surface and Pickup Solve - Fixed an issue where Compound Lens geometry would be incorrect in some cases where solves were present on one or both of parent surfaces.
- Extraordinary Ray in Birefringent Material Unexpectedly TIRs due to Effective Index Calculation - Implemented an enhancement to the iterative routine for finding the effective index in birefringent media. This improvement will now allow the effective index calculations to succeed, without erroneous TIR errors, for more challenging systems.
- POP: Unexpected Irradiance Values when Resampling at Surfaces - Removed unnecessary normalization of the beam field values after the resampling process when the POP setting 'Resample after Refraction' is enabled at a surface. The resampling loop itself takes care of normalizations to conserve intensity, so this duplicate step was incorrect.
- Problem with Performance Analysis in STAR Module - Fixed an issue where ray tracing with STAR volumetric data would not properly trace rays when the STAR effects are toggled off for one or more surfaces and the field type is real or paraxial image height. The STAR Performance Analysis window could show incorrect results as a result when using real or paraxial image height.
- Buttons not responsive after closing EOM - Fixed an issue where the Export to Speos Reduced Order Model could cause some OpticStudio buttons to become unresponsive.
- Index of SILICON became negative in Mirror space - Display of negative refractive index for mirrors in the ISO Drawing has been corrected. Quality of the ISO Drawing generation for mirrors has been improved.
- Pilot beam parameters are different depending on how Laguerre beam DLL is called - Fixed some possible inconsistent behavior in pilot beam parameters for beam DLLs when used in Physical Optics Propagation.
- Crash when doing Monte-Carlo Analysis - Fixed some cases where using TEDX/TEDY/TEDR or TETX/TETY/TETZ operands in tolerancing could cause a crash.
- Boolean Native Causes OS To Hang Indefinitely in NS Ray Trace - Fixed a corner case where the NSC ray tracer can get ‘stuck’ tracing a ray through a nearly co-planar surface.
- Crash when Docking Slider Window - Fixed an issue where docking a Slider window could cause a crash.
- STAR: Component RBMs tool does not change location of volumetric nodes except for volumetric data on the first surface of the component - Fixed an issue where removing component RBMs would not adjust volumetric data that was not attached to the first surface of the component.
- STAR: Component RBMs GUI becomes unresponsive when defining a component which includes the image surface - Fixed an issue where defining a STAR component that included the image surface would cause the software to become unresponsive.
- ROM export is wrong when does not save wavelength setting - Fixed some cases where the Export to Reduced Order Model to Speos results would be incorrect due to the wavelength not being saved.
- Reversal tool fails to reverse curvature in mirror space - Fixed some cases for the Reverse Elements Tool where surfaces could have the incorrect sign for curvature and where the back focal length of the reversed system could have the incorrect sign.
- Path Analysis: display an error message if no ZRD even if there is a PAF file - The Path Analysis tool now checks for a valid default PAF file in addition to a ZRD file and will not display an error if a valid default PAF file is found.
- Wavefront Slowdown - After the introduction of the True Freeform surface type, a problematic change degraded the calculation speeds for analyses such as Wavefront Map for sequential systems that include Grid Sag surfaces with no Zernike components.
- NSC 3D Layout experiencing issues with phosphors and fluorescence - Fixed issues where the wavelength was not properly stored in a ZRD file for phosphor & fluorescence bulk scattering and the phosphor & fluorescence emission spectrum was generating incorrectly.
- FFT MTF crashing consistently - Fixed a crash in FFT MTF when the wavelength weight is zero. This crash was only occurring since the 2024 R2 release.

