Hello Team,
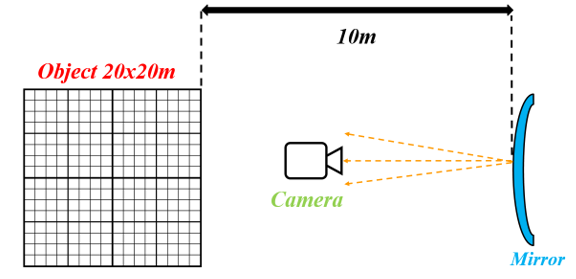
I want to know the image formation reflected from the convex mirror as shown below, but I am having trouble with the image simulation program. Could you please help me?
My design is attached zipped file. Thank you.
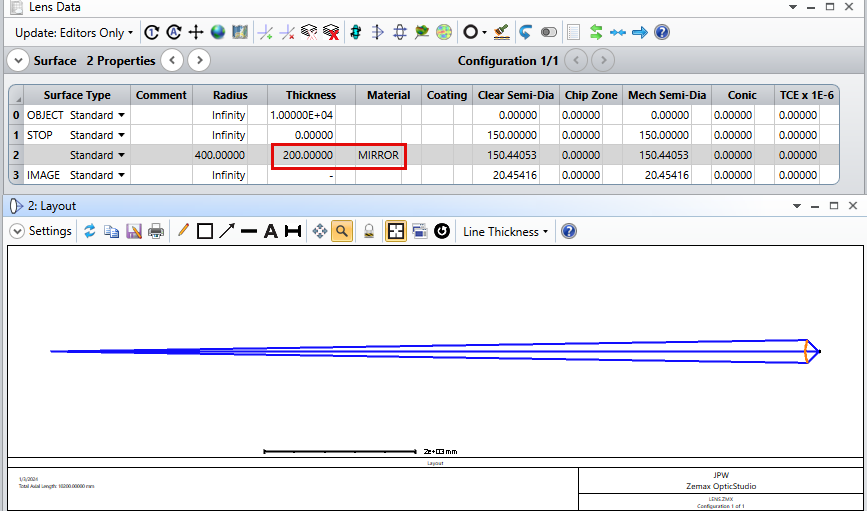
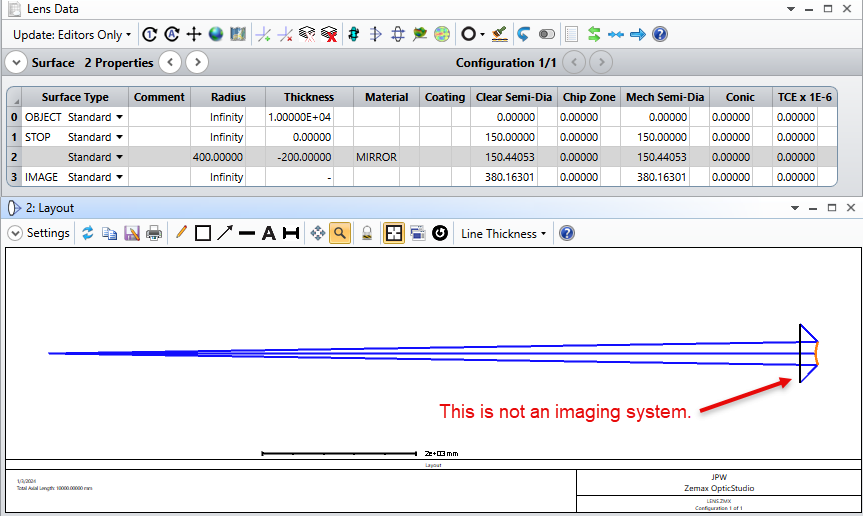
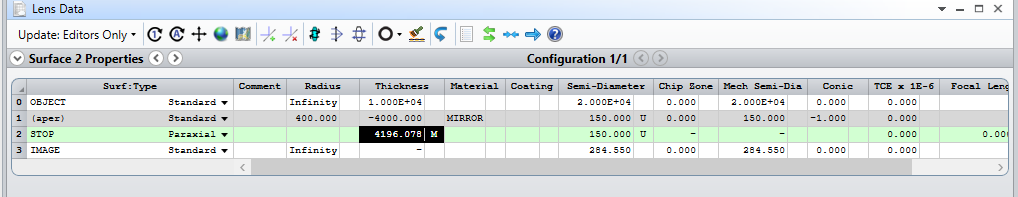
Configuration: An image (20x20 m) is placed in front of a convex mirror (ROC = 400 mm, Diameter = 300 mm) at a distance of 10m. And I want to know the image reflected by the mirror.