In Zemax, the Q-type Freeform surface is defined as:
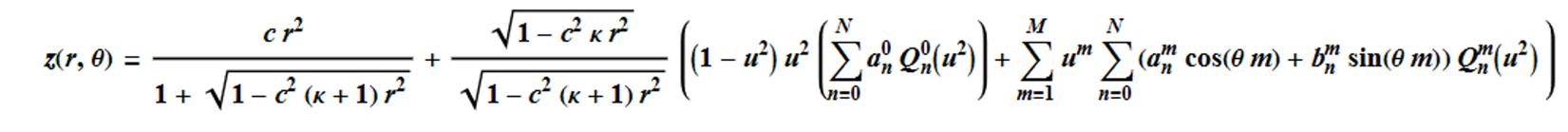
In the above equation, c is the vertex curvature, k is the conic constant, u = r/Un where r is the radial coordinate on the surface in lens units, and Un is the Norm Radius value for the surface.
The polynomial terms are chosen to minimize the departure of the surface gradient from the surface normal of the best-fit sphere, as described in the paper:
G. W. Forbes, Characterizing the shape of freeform optics. Optics Express, Vol. 20 No. 3, 30 January 2012, pages 2483 – 2499.
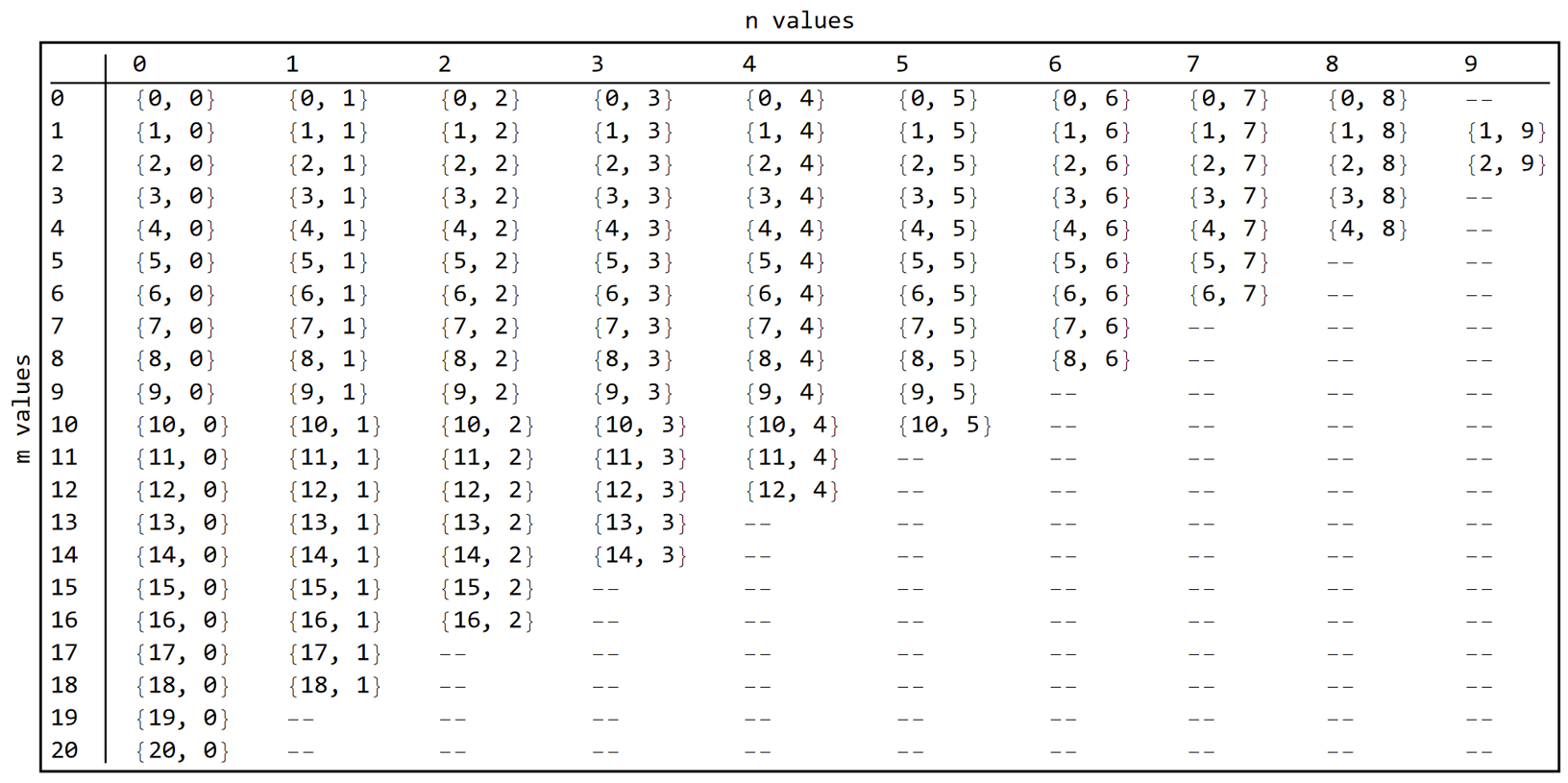
The Max Polynomial Radial Power column gives the maximum power of u included in the equation of the full surface. Powers of u up to 20 are allowed and the corresponding allowed values of m and n are listed below. (There are 229 coefficients if the order of u is 20.)
The full sets of Q polynomials can be derived using the following two equations, where delta is the Krönecker delta function, equal to 1 if n = n’ and 0 if n ¹ n’.
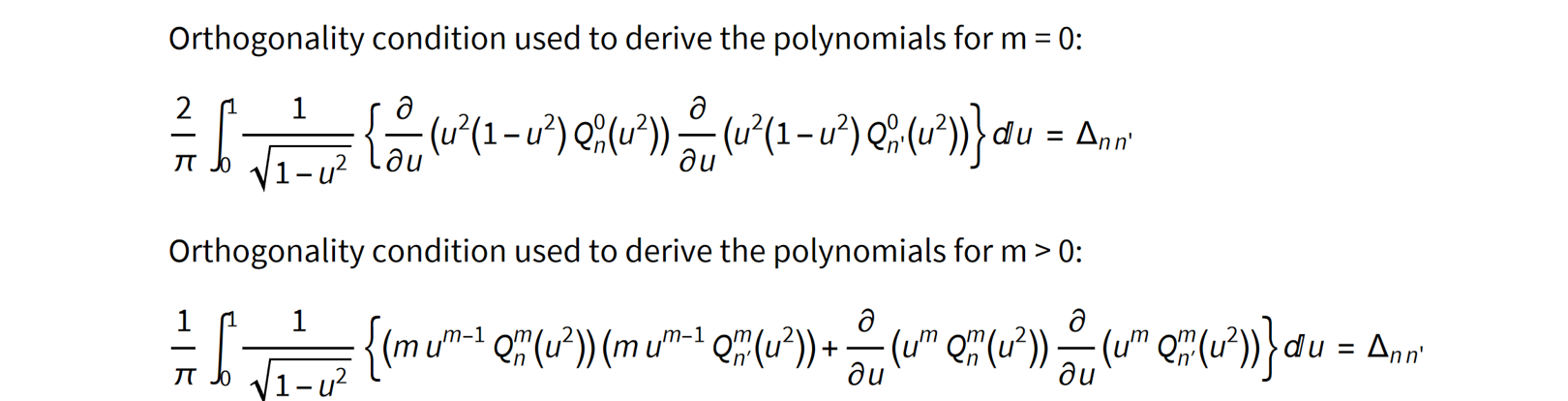
If we propose a generic polynomial form for each case, cmn, then the coefficients can be found by applying the orthonormality conditions. For example, for:

And then for the next case:
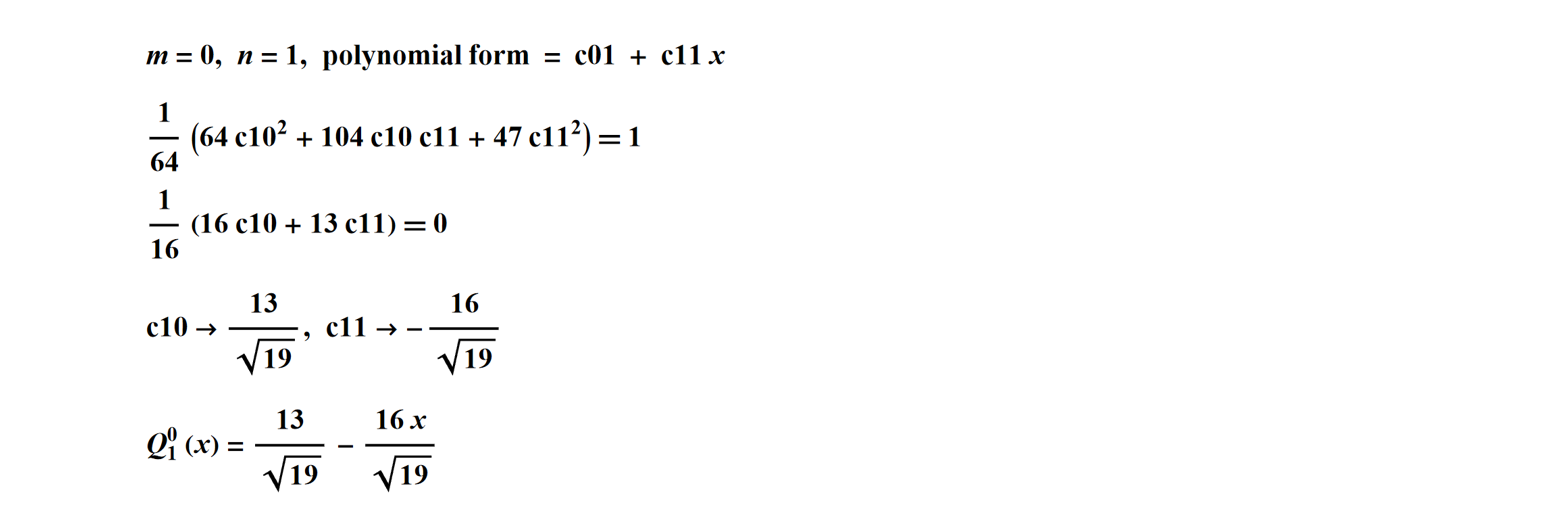
There are two solutions in each case that have opposite signs, and we choose the solution with the constant term > 0.
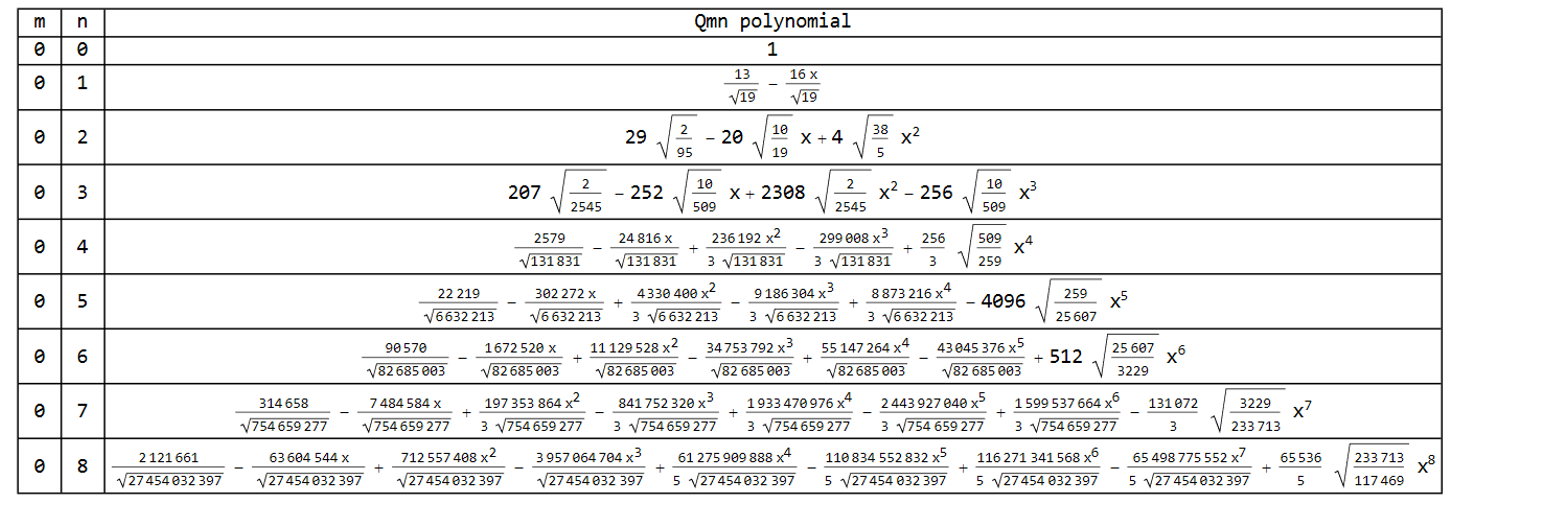
A complete list of the polynomials is in the attached file, QTypeFreeform_ListOfPolynomialForms_ForPosting.nb, which can be viewed with the free Wolfram Player: https://www.wolfram.com/player/. The polynomial forms are listed in a separate table for each value of m, as shown below for m = 0.
Each sum in the full surface equation (listed above) is given in QTypeFreeform_ListOfFullSurfaceEquations_ForPosting.nb, in both (r,q) and (x,y) formats.
Each term in the surface summation is given in full, like the three terms shown below, so that the individual entries can be summed as needed to create the final, complete surface equation.
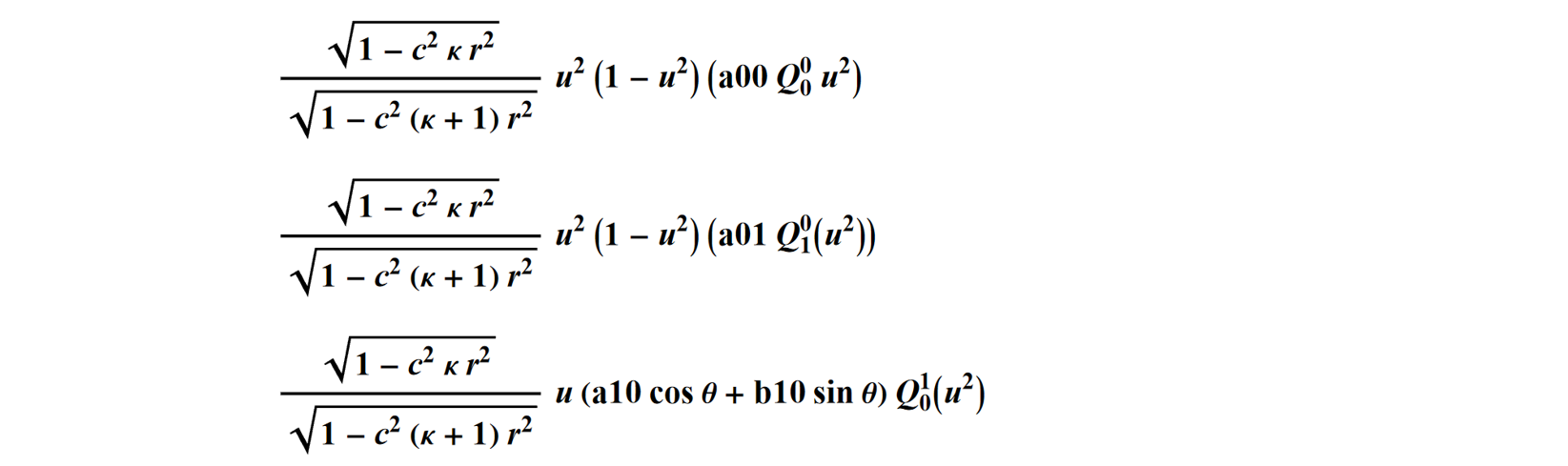
Each term is given in a table that shows all terms for a given value of m. The first two terms for m=0 are shown below.
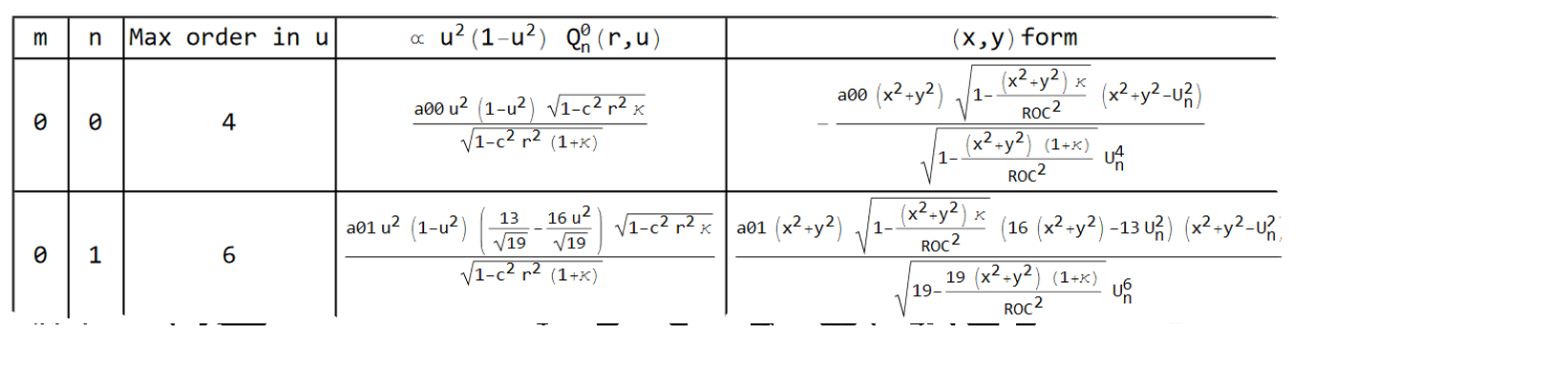
The powers in u are included in the tables so that the equations can be sorted and selected based on the Max Polynomial Radial Power value. Note that the order of coefficients in the LDE changes depending on the max power in u that is chosen. To find all the parts of the full surface equation, search every table to find all polynomials where u^p is less than or equal to the Max Polynomial Radial Power value, and sum all terms.
Attached files:
Listing of the Q-type freeform polynomials: QTypeFreeform_ListOfPolynomialForms_ForPosting.nb
QTypeFreeform_ListOfPolynomialForms_ForPosting.pdf
Listing of the full surface equations:
QTypeFreeform_ListOfFullSurfaceEquations_ForPosting.nb
QTypeFreeform_ListOfFullSurfaceEquations_ForPosting.pdf





