Hi All,
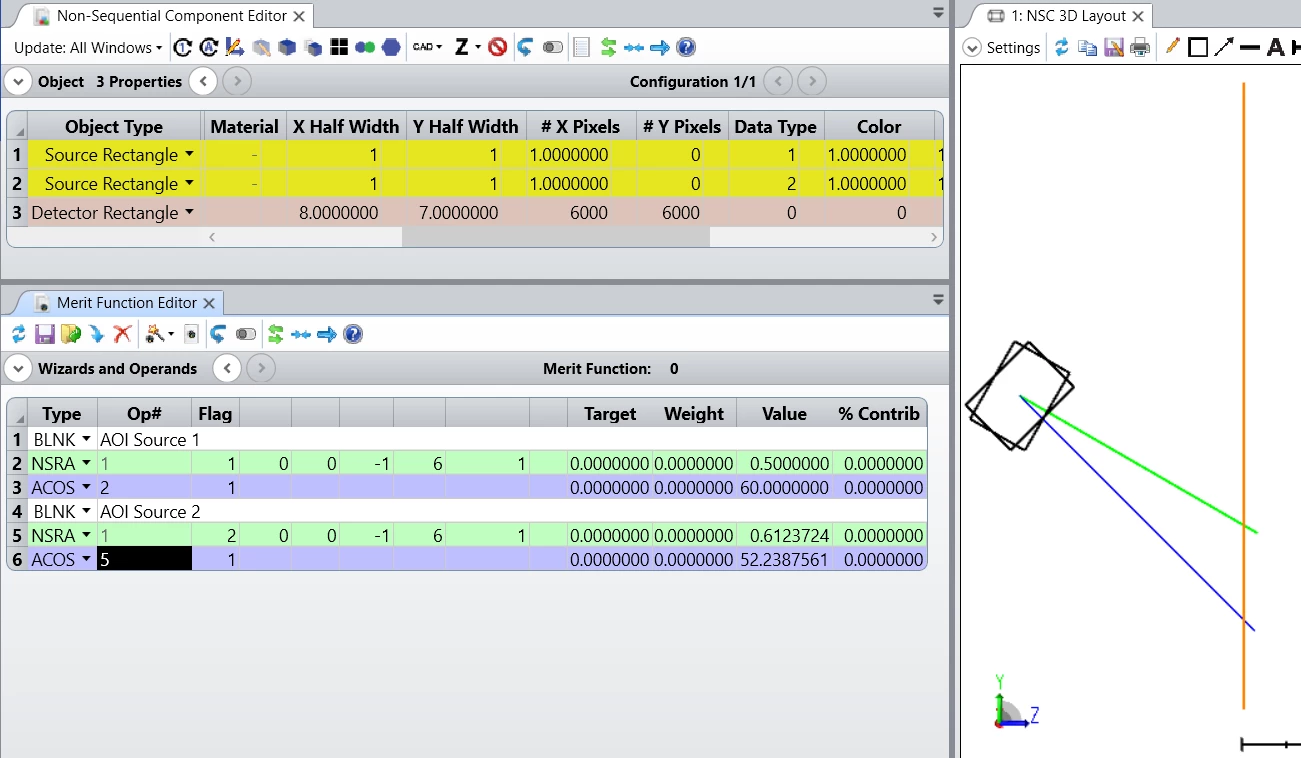
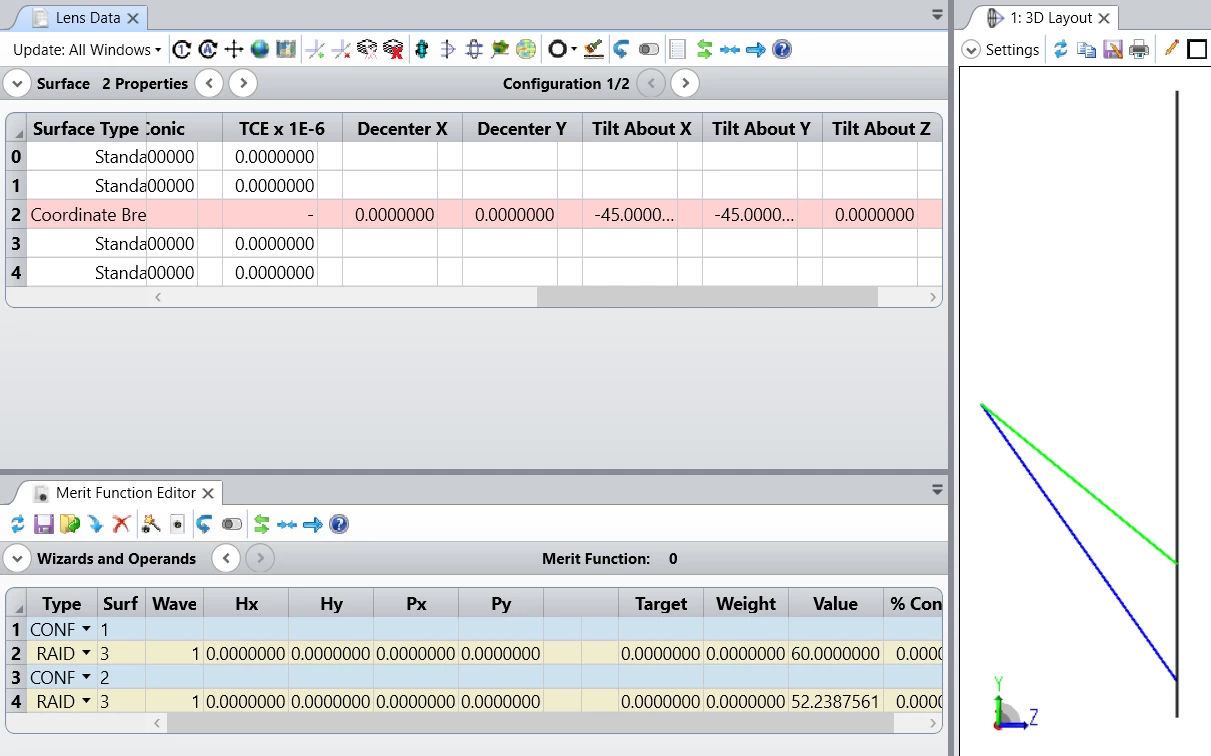
I am modeling optical system where there is a need to know the angles of the propgating rays after reflection, diffraction etc.
However, when using the Detector viewer/radiance space, I found different angles than anticipated.
For example, propagating free rays with tilt x 30, tilt y 20- I got: 21, 28.8 at the detector(attached here):
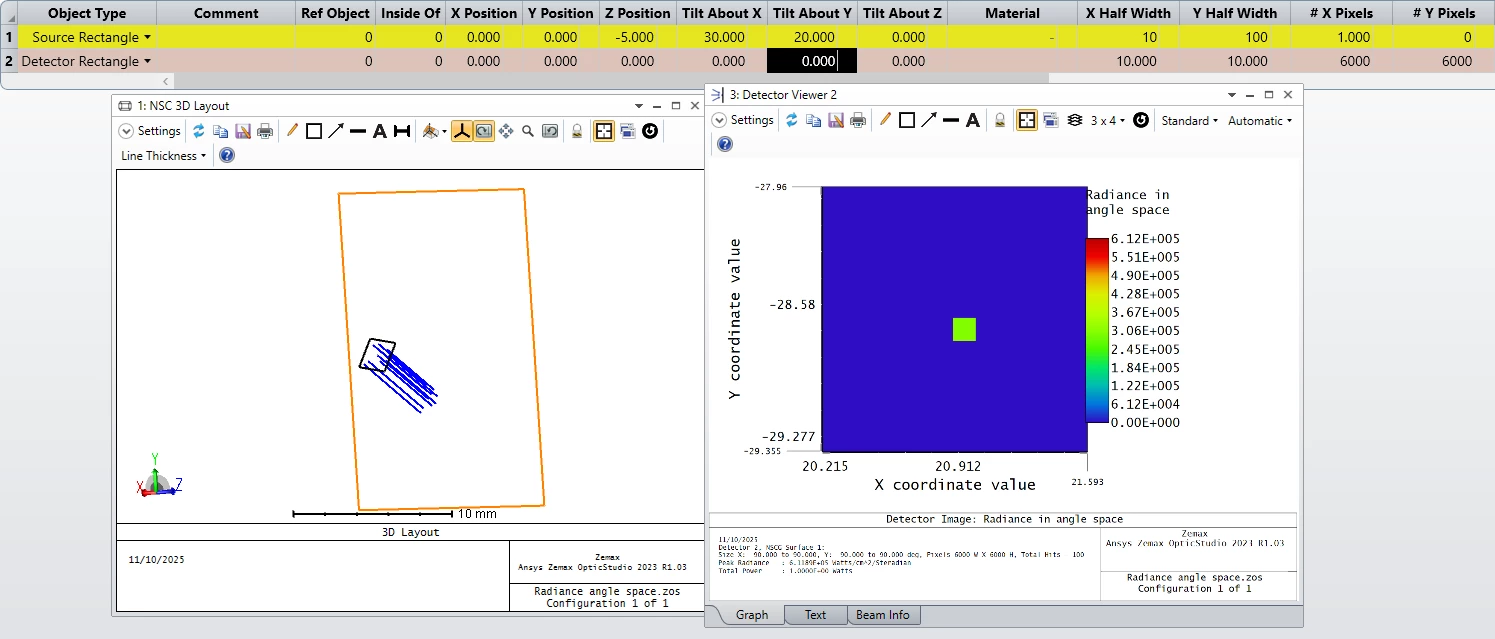
What happend?
Thanks,
Nadav