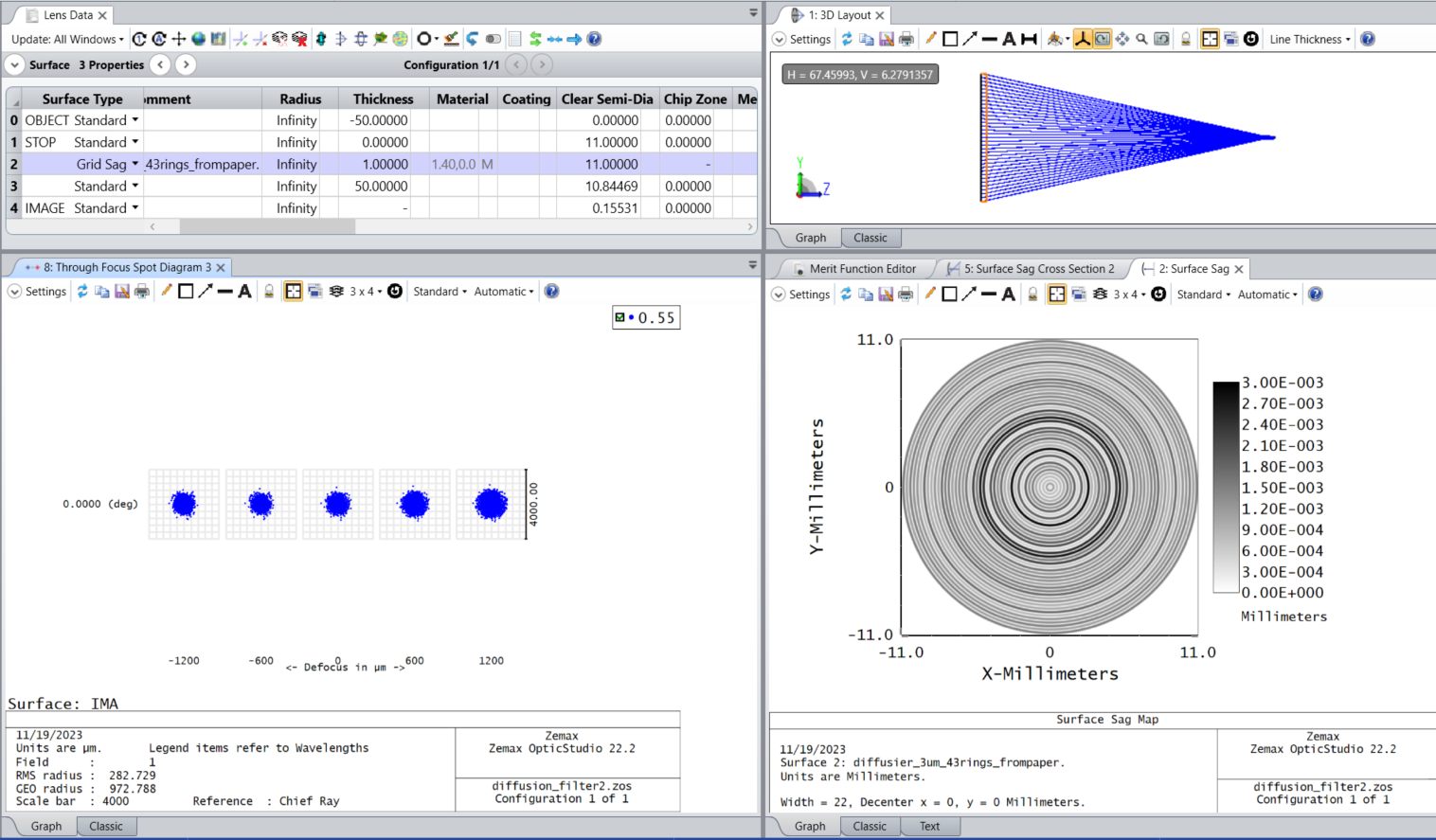
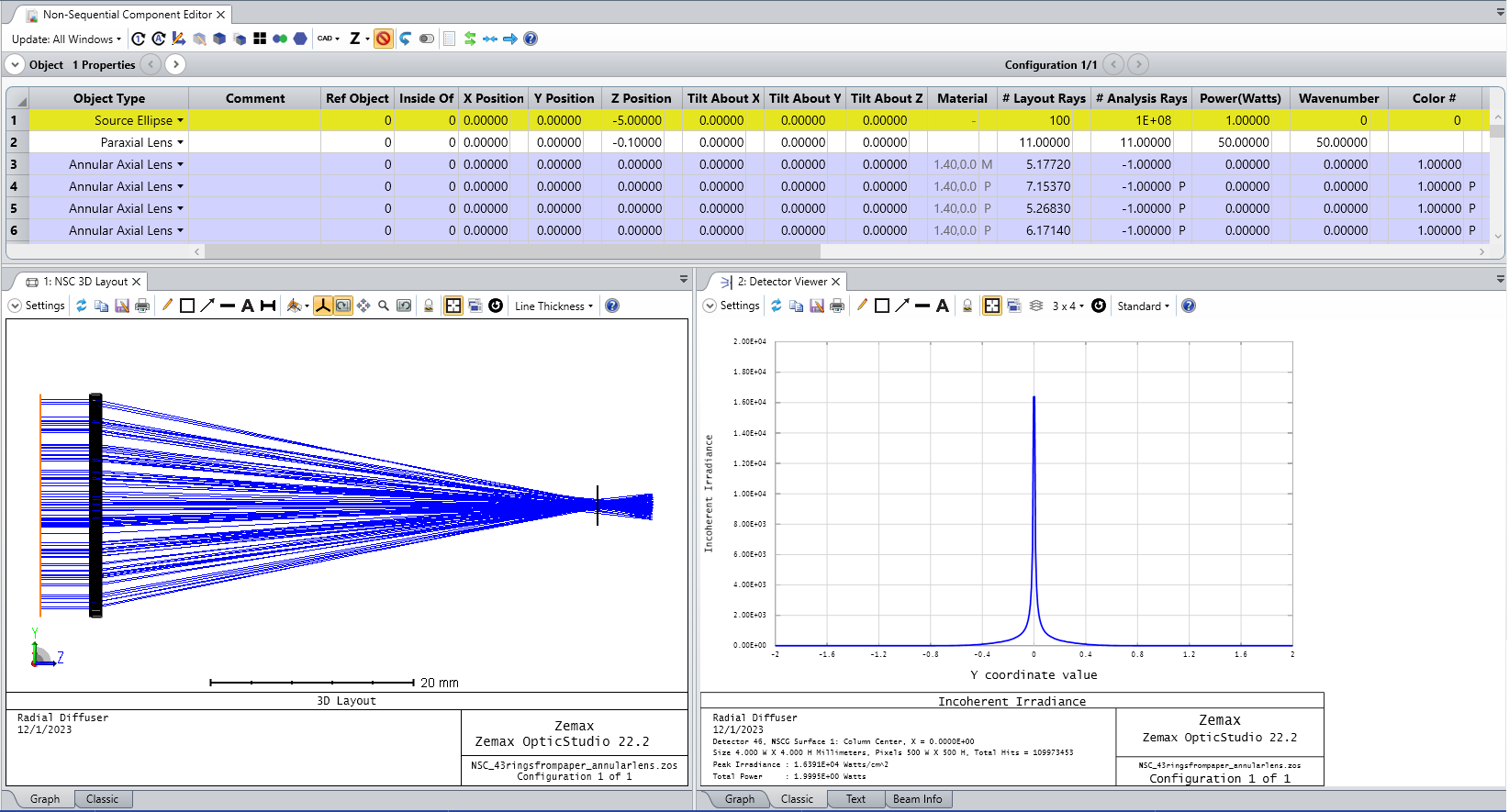
Hello all,
I would like to model a radially symmetric diffuser shown below in Zemax. Any thoughts or recommendations on how to accomplish this? I’m hoping there is an efficient approach that takes advantage of the radial symmetry, and I’m not forced to create this as a 2D grid phase or grid sag surface.
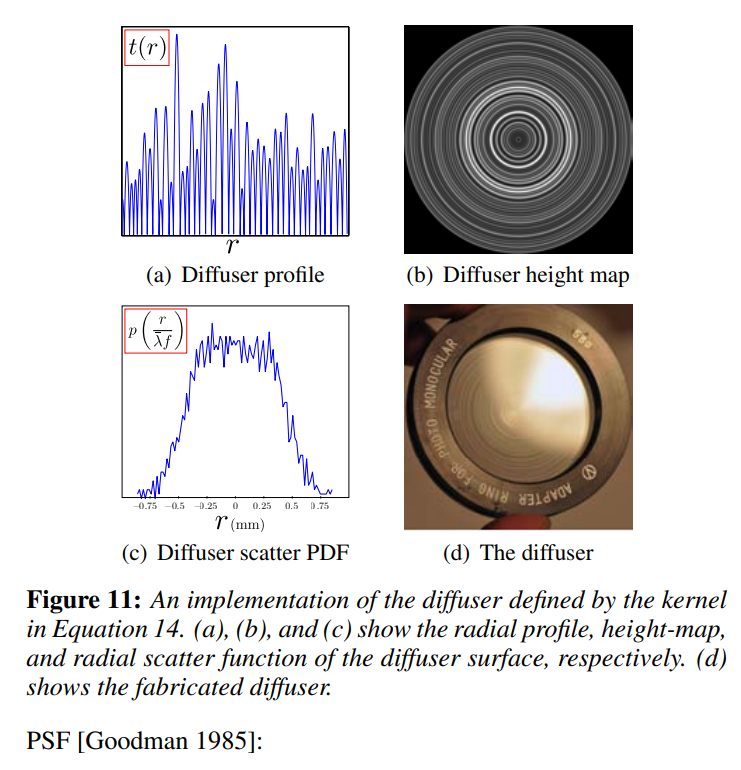
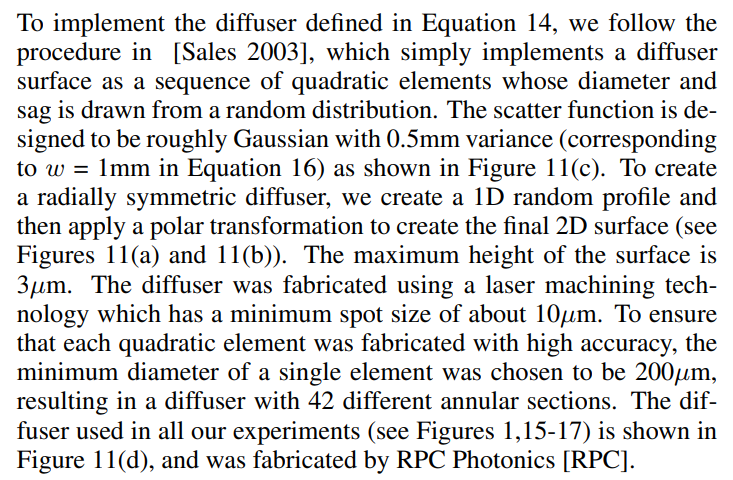
The most relevant section from the attached paper is below.
Thanks in advance for your help,
John