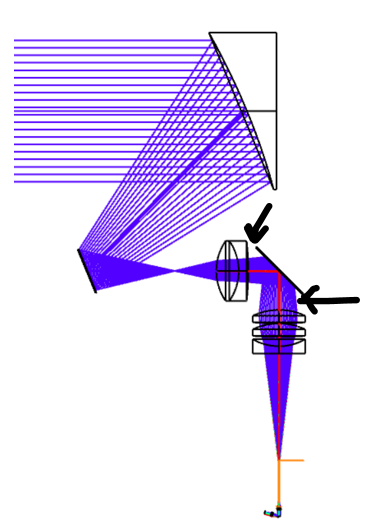
Hi again Fatimeh,
The IMSF operand is your friend. Check the docs, IMSF lets you define the image surface on the fly inside the merit function. So you can
IMSF {intermediate focus surface)
Default RMS Spot Size MF
IMSF {internal collimated space}
Default angular radius MF
IMSF {Final Surface}
Whatever your final Image Quality MF is.
It’s cool and exactly what you need for this kind of problem. When using the Optimization Wizard, use the ‘Start at’ control to make it write the intermediate merit functions without overwriting each other. I think there’s a KB article on intermediate surface optimization.