Hello!
help please, how to calculate the light collection efficiency of the lens?
light collection efficiency
Best answer by David
Hi Dmitriy,
For me, collection efficiency is still very dependent on context. In the attached file I constructed a simple example based on a particular situation: That of the suns rays being focused by a singlet onto a rectangular detector.
- The sun subtends an angle of 0.5 degrees, so a Source Two Angle with a 0.25 degree half angle is used to simulate the suns rays. It has an elliptical shape in position and angle space and is slightly larger than the collection lens.
- A singlet is used to focus the rays onto the detector. Both the front and back radii are variable in optimization.
- A Detector Surface is used to measure the power hitting the lens. Its diameter and radius are forced to match the lens by pick ups. It is placed just in front of the lens. It is set to Front Only so it does not detect back reflection from the lens.
- A Detector Rectangle is placed at a fixed distance from the lens to represent a physical detector. For other shapes an aperture could be placed in front of it, or a Detector Surface could be used for a disc.
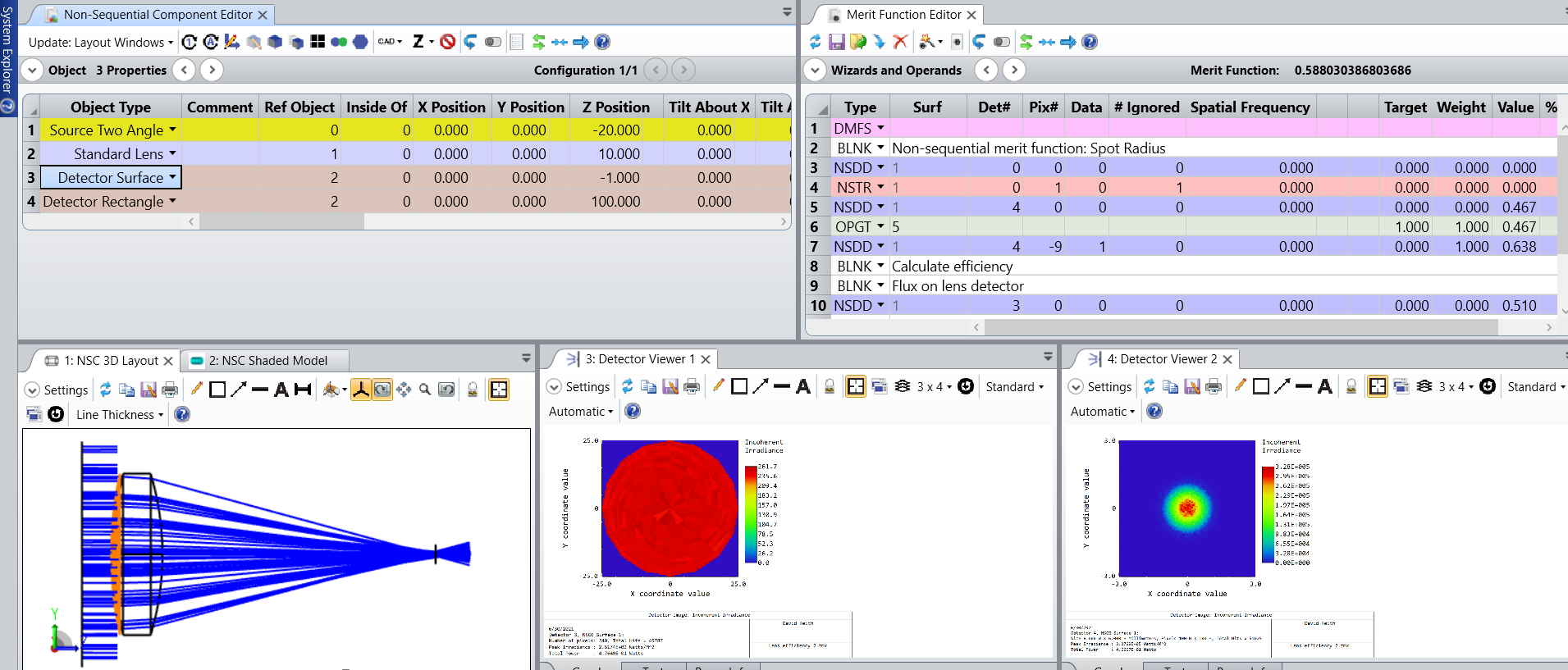
The Merit Function Wizard was used to create a merit function that seeks to minimize the spot size on detector 4 while also seeking to maximize the power. To this was added operands to obtain the power on the lens detector 3 and then divide the total power on detector 4 by that on detector 3.
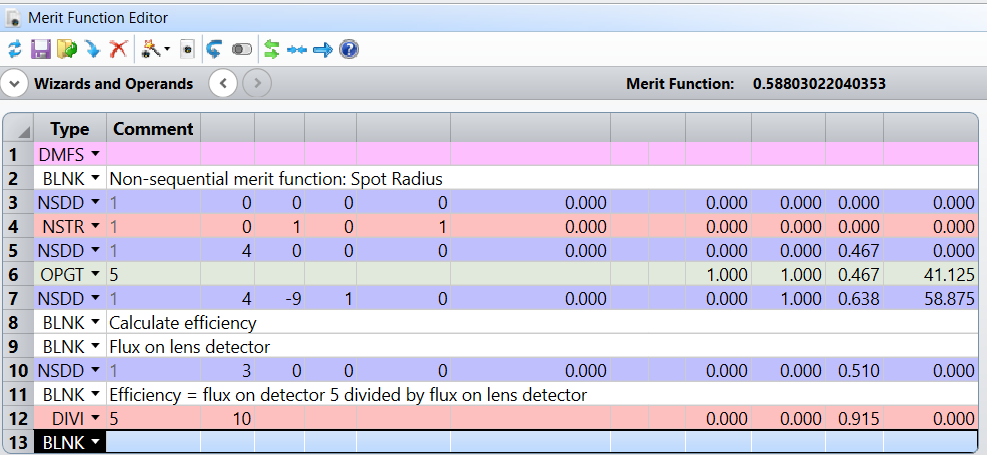
Optimization was done by Orthoganal Descent. This determined the radii of the front and back of the lens, and a collection efficiency of 0.915. For this case, the major loss is certainly the Fresnel reflections of the two faces of the lens. (For real detectors, it might be best to fill the detector more uniformly and not produce a hot spot.)
I hope this helps,
Kind regards,
David
Enter your E-mail address. We'll send you an e-mail with instructions to reset your password.




