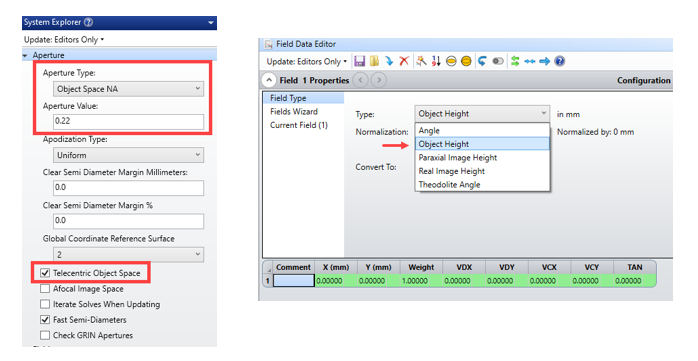
I have an optical fiber bundle with core diameter 910 microns and NA = 0.22 and I would like to make the source as the optical fiber output end with rays coming out of this fiber. The objective of this simulation is to get a collimated rays at the image plane by using a collimating lens. Since I am using a fiber bundle the rays from the farthest point cannot be collimated easily so there would some losses and I need to find how much is overall efficiency of this system.
My question is can I design the fiber output end by providing as many fields points to represent the fiber bundle and assume each point emits a cone of light with NA = 0.22. If not how can I model the fiber end as a source?